types of hypotonic solution
|
Study on the Effect of Different Hypotonic Solutions on
13-Feb-2013 temperature and type of hypotonic solution employed varies. Over treatment leads to over spreading with rupture of cell. |
|
Management of IV Fluids and Electrolyte Balance
Understand osmolarity and the classification of solutions as hypertonic isotonic and hypotonic hospital receive some type of IV therapy. |
|
Methods of adjusting tonicity and pH values of some drugs and
Tonicity is generally classified in three types: 1. Hypertonicity. 2. Hypo tonicity. 3. Isotonicity. Hypertonic isotonic and hypotonic solutions are. |
|
Reflex Circulatory Effects Elicited by Hypertonic and Hypotonic
Hypotonic Solutions Injected into Femoral and of hypertonic saline solution produced pro- ... Three types of denervation experiments were. |
|
IV Fluids
02-Sept-2021 When administering IV fluids the type and amount of fluid may influence ... Hypotonic solutions have a concentration of dissolved particles ... |
|
Efficacy and Safety of Isotonic and Hypotonic Intravenous
08-Sept-2021 hyponatraemia while hypotonic solution increases the risk of ... in the types of maintenance fluid during the study period for risks of ... |
|
Hypo-Hyper-Iso-notes-2h3zgci.pdf
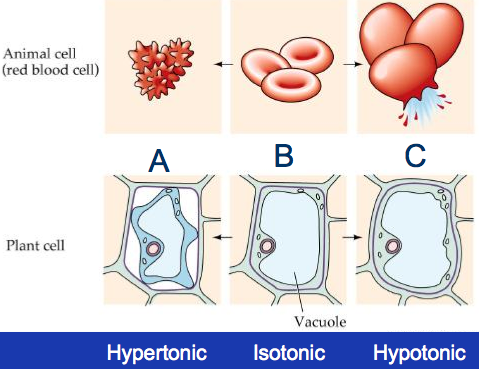
3 Types of Solutions: • Hypotonic Solution. • Isotonic Solution. • Hypertonic Solution. Page 4. Hypotonic Solution. (HYPO = the cell is going to BLOW). |
|
BIOLOGY CLASS 9 date: 07.04.2020
07-Apr-2020 b) Hypotonic solution- If a medium surrounding a cell is more ... 1) Plant cell kept in different types of solutions-. |
|
Untitled
In a hypotonic solution animal cells experience osmosis and a pressure builds up in Identify the type of solution (isotonic |
|
Management of IV Fluids and Electrolyte Balance
Hypotonic • A hypotonic solution shifts fluid out of the intravascular compartment hydrating the cells and the interstitial compartments Osmolarity is lower than serum osmolarity Isotonic • Because an isotonic solution stays in the intravascular space it expands the intravascular compartment Osmolarity is the same as serum osmolarity |
What Are IV Fluids?
Intravenous fluids (IV Fluids), also known as intravenous solutions, are supplemental fluids used in intravenous therapy to restore or maintain normal fluid volume and electrolyte balance when the oral route is not possible. IV fluid therapy is an efficient and effective way of supplying fluids directly into the intravascular fluid compartment, in ...
Types of IV Fluids
There are different types of IV fluids and different ways on how to classify them. The most common way to categorize IV fluids is based on their tonicity: 1. Isotonic. Isotonic IV solutions that have the same concentration of solutes as blood plasma. 2. Hypotonic. Hypotonic solutions have lesser concentration of solutes than plasma. 3. Hypertonic. ...
Crystalloids
Crystalloid IVsolutions contain small molecules that flow easily across semipermeable membranes. They are categorized according to their relative tonicity in relation to plasma. There are three types: isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic.
Colloids
Colloids contain large molecules that do not pass through semipermeable membranes. Colloids are IV fluids that contain solutes of high molecular weight, technically, they are hypertonic solutions, which when infused, exert an osmotic pull of fluids from interstitial and extracellular spaces. They are useful for expanding the intravascular volume an...
See Also
Here are other nursing pharmacology study guides: 1. Nursing Pharmacology – Study Guide for Nurses Our collection of topics related to nursing pharmacology 2. Pharmacology Nursing Mnemonics & Tips These nursing mnemonics aim to simplify the concepts of pharmacology through the use of a simple, concise guide. 3. Generic Drug Name Stems Cheat Sheet L...
What is the difference between hypotonic and hypertonic solutions?
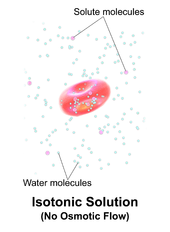
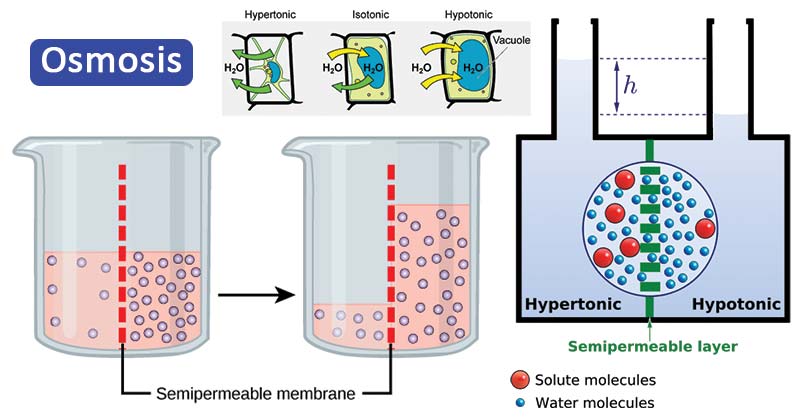
In a hypotonic solution, the extracellular fluid has a lower osmolarity than the fluid inside the cell; water enters the cell. In a hypertonic solution, the extracellular fluid has a higher osmolarity than the fluid inside the cell; water leaves the cell.
What is an example of a hypotonic IV solution?
An example of a hypotonic IV solution is 0.45% Normal Saline (0.45% NaCl). When hypotonic IV solutions are infused, it results in a decreased concentration of dissolved solutes in the blood as compared to the intracellular space. This imbalance causes osmotic movement of water from the intravascular compartment into the intracellular space.
How does water move in a hypotonic solution?
Water moves from the side of the membrane with lower osmolarity (and more water) to the side with higher osmolarity (and less water). In a hypotonic solution, the extracellular fluid has a lower osmolarity than the fluid inside the cell; water enters the cell.
How does hypotonic fluid affect homeostasis?
Hypo- means low which, in the case of IV fluids, has fewer solutes and has more fluid. This will cause the fluids to move inside the cell, resulting in the expansion or swelling of the cell. Since the osmolality of hypotonic solutions is lower, the fluid from outside of the cell enters inside the cell to achieve homeostasis.
|
IV Fluids - NursingCentercom
2 jan 2019 · When administering IV fluids, the type and amount of fluid may Hypotonic solutions have a concentration of dissolved particles lower |
|
Hypo, Hyper, Iso Notes
3 Types of Solutions: • Hypotonic Solution • Isotonic Solution • Hypertonic Solution What type of solution are these cells in? Hypertonic Hypotonic Isotonic |
|
Isotonic versus hypotonic solutions for maintenance - UQ eSpace
Secondly, to compare the risk of hypernatraemia, the effect on mean serum sodium concentration and the rate of attributable adverse effects of both fluid types in |
|
FLUID AND BLOOD THERAPY
Recognize examples of hypertonic, isotonic, and hypotonic crystalloids solutions Describe the proper patient management for the three major types of blood |
|
Management of IV Fluids and Electrolyte Balance
extracellular fluid • Understand osmolarity and the classification of solutions as hypertonic, isotonic and hypotonic hospital receive some type of IV therapy |
|
Fluid and Electroly te Series - CEConnection
and hypertonic crystalloid solutions in detail ISOTONIC volume 6 Types of isotonic solutions include 0 9 Types of hypotonic fluids include 0 45 sodium |
|
Study on the Effect of Different Hypotonic Solutions on
13 fév 2013 · The time of exposure to hypotonic treatment is critical as the concentration, temperature and type of hypotonic solution employed varies |



![PDF] Isotonic versus hypotonic solutions for maintenance PDF] Isotonic versus hypotonic solutions for maintenance](https://bmjpaedsopen.bmj.com/content/bmjpo/3/1/e000385/F1.large.jpg)