an introduction to random matrices
|
Introduction to Random Matrices Theory and Practice
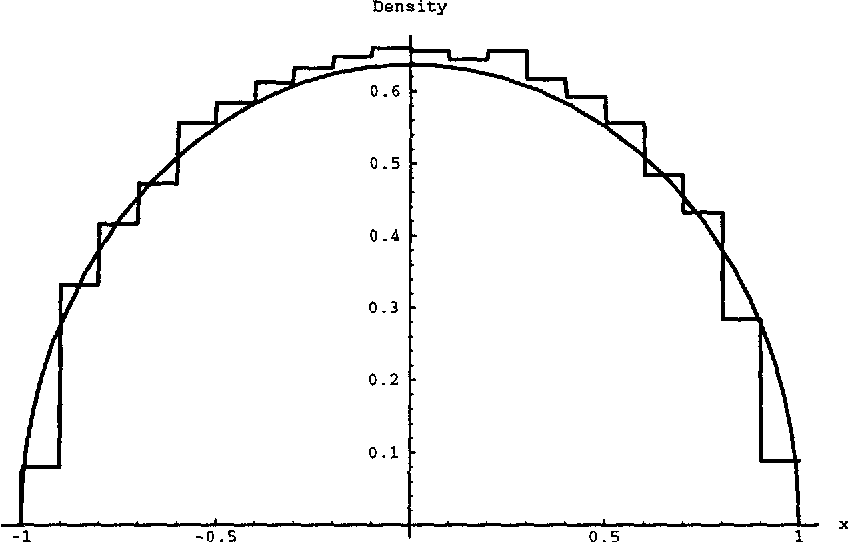
In this Chapter we introduce the so called resolvent a complex function from which the spectral density1 can be calculated The advantage of the resolvent approach is that one has to solve an algebraic equation (like ax2+bx+c = 0) instead of a (singular) integral equation (like Pr R |
|
An Introduction to Random Matrices
An Introduction to Random Matrices The theory of random matrices plays an important role in many areas of pure mathematics and employs a variety of sophisticated mathematical tools (analytical probabilistic and combinatorial) This diverse array of tools while attesting to the |
|
An Introduction to Random Matrices
University of Minnesota and Weizmann Institute of Science copyright information here To Meredith Ben and Naomi |
What are some examples of limiting models in random matrix theory?
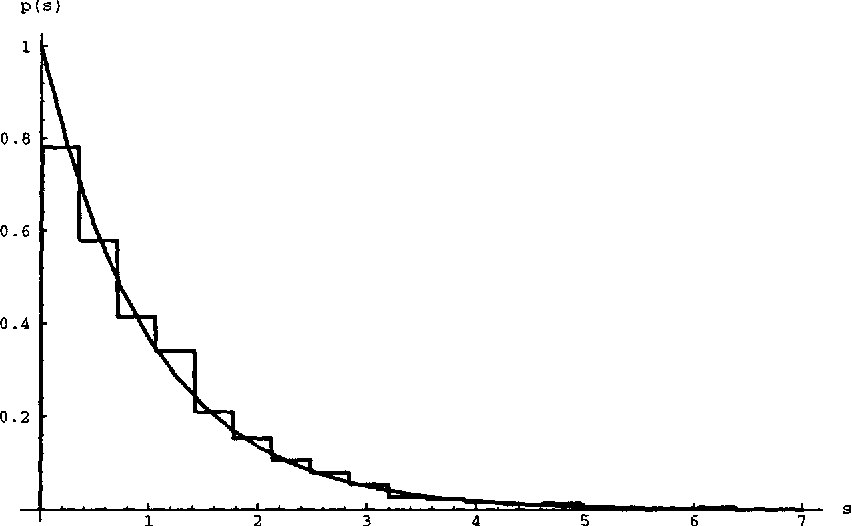
Similar kernels arise in various limiting models in random matrix theory. For instance, the Bessel kernel { corresponding to f(x) = J (x), the Bessel function with parameter { describes uctuations about the singular values of random positive de nite Hermitian matrices. Theorem 9. For each interval (a; b) R, 1
What is a random matrices theory?
The theory of random matrices plays an important role in many areas of pure mathematics and employs a variety of sophisticated mathematical tools (analytical, probabilistic and combinatorial).
What is a random matrix xn?
In that setting, a random matrix XN is a measurable map from (W,F) to MatN(F). Our main interest is in the eigenvalues of random matrices. Recall that the eigenvalues of a matrix H ∈ MatN(F) are the roots of the characteristic polynomial PN(z) = det(zIN − H), with IN the identity matrix.
What are some good books about random matrices?
Providence, R.I., American Mathematical Society, fourth edition, 1975. Colloquium Publications, Vol. XXIII. [Tal96] M. Talagrand. A new look at independence. Annals Probab., 24:1–34, 1996. [TaV08a] T. Tao and V. H. Vu. Random matrices: the circular law. Commun. Contemp. Math., 10:261–307, 2008.
Ofer Zeitouni
University of Minnesota and Weizmann Institute of Science copyright information here To Meredith, Ben and Naomi cims.nyu.edu
Preface
The study of random matrices, and in particular the properties of their eigenval-ues, has emerged from the applications, first in data analysis and later as statisti-cal models for heavy-nuclei atoms. Thus, the field of random matrices owes its existence to applications. Over the years, however, it became clear that models related to random matrice
2.1.7 Central limit theorems for moments
Our goal here is to derive a simple version of a central limit theorem (CLT) for linear statistics of the eigenvalues of Wigner matrices. With XN a Wigner matrix and LN the associated empirical measure of its eigenvalues, set WN,k := N[hLN,xki−h ̄ LN,xki]. Let cims.nyu.edu
2.5 Joint distribution of eigenvalues in the GOE and the GUE
We are going to calculate the joint distribution of eigenvalues of a random sym-metric or Hermitian matrix under a special type of probability law which displays a high degree of symmetry but still makes on-or-above-diagonal entries indepen-dent so that the theory of Wigner matrices applies. cims.nyu.edu
P(b)
is said to belong to the Gaussian orthogonal ensemble (GOE) or the cims.nyu.edu
U ∈ U
N . Given a positive integer r and subsets I,J as above, put r r cims.nyu.edu
=: PN,1 ×PN,2,
where we used the fact that li ≥ lj and xi,N xj,N. ≥ Õ cims.nyu.edu
3.2 Hermite polynomials and the GUE
In this section we show why orthogonal polynomials arise naturally in the study of the law of the GUE. The relevant orthogonal polynomials in this study are the Hermite polynomials and the associated oscillator wave-functions, which we in-troduce and use to derive a Fredholm determinant representation for certain prob-abilities connected with the G
Proof
Using the identity det(AB) = det(A)det(B) applied to cims.nyu.edu
= (N − p)/N. ⊓⊔
Now we arrive at the main point, on which the study of the local properties of the GUE will be based. cims.nyu.edu
3.3.1 Calculation of moments of LN ̄
In this section, we derive the following explicit formula for h ̄ LN,es i. cims.nyu.edu
G(x,y) H(k) (x,y)
i = F(x,y)−G(x,y) F(x,y) if i < k, if i = k, if i > k, noting that, by the linearity of the determinant with respect to rows, cims.nyu.edu
K ⋆R = R−K = R⋆K .
It is helpful if not perfectly rigorous to rewrite the last formula as the operator identity cims.nyu.edu
3.5.1 The method of Laplace
Laplace’s method deals with the asymptotic (as s → ¥) evaluation of integrals of the form cims.nyu.edu

Random Matrices: Introduction

Random Matrices: Theory and Practice

Introduction to Random Variables
|
An Introduction to Random Matrices
An Introduction to Random Matrices. Greg W. Anderson. University of Minnesota. Alice Guionnet. ENS Lyon. Ofer Zeitouni. University of Minnesota and Weizmann |
|
An Introduction to Random Matrices
2 mai 2015 has been to present a rigorous introduction to the basic theory of ... So what is a random matrix and what questions are we about to study? |
|
Introduction to random matrices UNFINISHED
These lectures are devoted to a simple introduction to Random Matrix Theory iii) Random matrices and statistical mechanics models on “random lattices”. |
|
MATH 247A: INTRODUCTION TO RANDOM MATRIX THEORY 1
MATH 247A: INTRODUCTION TO RANDOM MATRIX THEORY. TODD KEMP. CONTENTS. 1. Wigner Matrices define a sequence of symmetric random matrices Yn by. [Yn]ij =. |
|
Introduction to Random Matrices Theory and Practice
21 déc. 2017 Introduction to Random Matrices ... So what is a random matrix? ... pedagogical introduction to the Gaussian ensembles |
|
CORRECTION SHEET AN INTRODUCTION TO RANDOM
24 janv. 2019 AN INTRODUCTION TO RANDOM MATRICES. Anderson Guionnet |
|
CORRECTION SHEET AN INTRODUCTION TO RANDOM
24 janv. 2019 AN INTRODUCTION TO RANDOM MATRICES. Anderson Guionnet |
|
Free Probability and Large N Limit 1
Introduction to Random Matrices from a physicist's perspective Random matrices: a major theme in theoretical physics since Wigner (1951);. |
| An introduction to random matrix theory |
|
Introduction to random matrices
These notes provide an introduction to that aspect of the theory of random matrices dealing with the distribution of eigenvalues. To first orient the reader we |
|
An Introduction to Random Matrices - The Faculty of Mathematics
An Introduction to Random Matrices Greg W Anderson University of Minnesota Alice Guionnet ENS Lyon Ofer Zeitouni University of Minnesota and |
|
Introduction to random matrices UNFINISHED - LPTHE
These lectures are devoted to a simple introduction to Random Matrix Theory ( RMT) Let us start with a definition which is a tautology A RMT is a theory in which |
|
NOTES FROM INTRODUCTION TO RANDOM MATRICES BY
Recall the definition of Ln the empirical distribution of the eigenvalues for the Wigner matrix Let ¯Ln = E (Ln) be the (non-random) measure on R given by ¯Ln( a, b) |
|
Introduction to Random Matrices
III we introduce the invariant measures for the three “circular ensembles” involving unitary matrices We also define the level spacing distributions and express |
|
INTRODUCTION TO RANDOM MATRICES University of Havana
This lectures give a brief introduction to one aspect of random matrix theory, the asymptotic behavior of the eigenvalues of random Hermitian matrices as the |
|
Introduction to Random Matrix Theory from An Invitation to Modern
Definition 1 1 8 (Ensembles) A collection of matrices, along with a probability density describing how likely it is to observe a given matrix, is called |
|
Introduction to random matrices - UC Davis Mathematics
The Gaussian ensembles of random matrix theory can also be characterized as those measures that have maximum information entropy subject to the constraint of |
|
An introduction to random matrix theory
7 août 2015 · We shall introduce in Section 3 and 4 two ensembles of random matrices, but before that, let us pose the problem in mathematical terms 2 1 |
|
Lectures on Random Matrices - Imperial College London
nates Now we are ready to define our object of study Definition 1 A Wigner matrix ensemble is a random matrix ensemble of Hermitian matrices H = (Hij)n |