assumptions of linear programming ppt
|
Linear programming 1 Basics
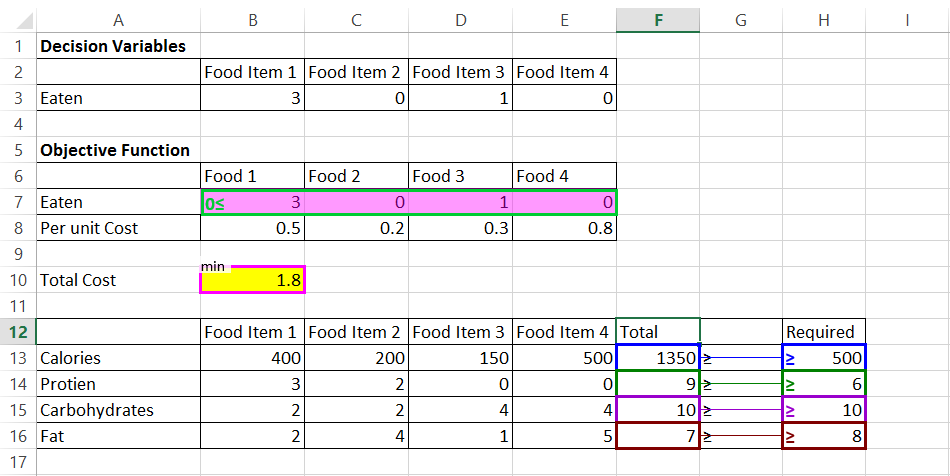
Linear Programming deals with the problem of optimizing a linear objective function subject to linear equality and inequality constraints on the decision variables Linear programming has many practical applications (in transportation production planning ) It is also the building block for combinatorial optimization |
|
CHAPTER 11: BASIC LINEAR PROGRAMMING CONCEPTS
Nov 5 1998 · Linear programming can be defined as: “A mathematical method to allocate scarce resources to competing activities in an optimal manner when the problem can be expressed using a linear objective function and linear inequality constraints ” |
|
Basic Linear Programming Concepts
The Fundamental Assumptions of Linear Programming 1 Linear constraints and objective function a Proportionality: the value of the obj func and the response of each resource is proportional to the value of the variables b Additivity: there is no interaction between the effects of different activities 2 |
|
Lecture 5 1 Linear Programming
A linear program is an optimization problem in which we have a collection of variables which can take real values and we want to nd an assignment of values to the variables that satis es a given collection of linear inequalities and that maximizes or minimizes a given linear function |
What are the assumptions of linear programming?
Let us look at the other assumptions of linear programming: Linear programming assumes that any modification in the constraint inequalities will result in a proportional change in the objective function. This means that if it takes 10 hours to produce 1 unit of a product, then it would take 50 hours to produce 5 such products.
How do you write a linear programming problem?
Be sure to identify the units of the decision variables. On a separate piece of paper, write out the linear programming formulation of the problem. Include the units of the variables and the coefficients in your description. Don't forget the non-negativity constraints.
What are the conditions for a linear programming model?
As you know by now, a linear programming model has the following conditions: The decision variables must have a linear relationship. It must have an objective function. Resource constraints are required. It must have a non-negative constraint.
What is linear programming?
Linear programming is not a programming language like C++, Java, or Visual Basic. Linear programming can be defined as: “A mathematical method to allocate scarce resources to competing activities in an optimal manner when the problem can be expressed using a linear objective function and linear inequality constraints.”
What Is Linear Programming?
Linear programming is also a form of constrained optimisation, and quite possibly, the most commonly used. To understand the meaning of linear programming, we need to first understand what is meant by constrained optimisation. In constrained optimisation, we have to optimise the objective function (or find the best value of the function), keeping i
Introduction to Linear Programming
Linear Programming (LP) is one of the most widely used techniques for effective decision-making. It is an optimisation technique that focuses on providing the optimal solution for allocating available resources amongst different competing and conflicting requirements. The first serious attempt at the linear programming formulation and solution of a
Assumptions of Linear Programming
The first and foremost assumption when using linear programming to model the real world is that a linear model is suitable. This is an important point to consider, given the fact that the real world will have plenty of non-linear relationships. Let us look at the other assumptions of linear programming: 1. Proportionality / Linearity 2. Certainty 3
Properties of Linear Programming Model
As you know by now, a linear programming model has the following conditions: 1. The decision variables must have a linear relationship. 2. It must have an objective function. 3. Resource constraints are required. 4. It must have a non-negative constraint. A linear programming model involves an objective function, well-defined decision variables, an
Advantages of Linear Programming
There are several advantages of linear programming as mentioned below: 1. Scientific approach to problem-solving 2. Evaluation of all possible alternatives 3. Optimal utilisation 4. Helps in re-evaluation 5. Improves the quality of the decision 6. Addresses bottlenecks 7. Applicable to diverse problems 8. Formation of information base geektonight.com
Disadvantages of Linear Programming
While LP is a highly effective OR technique and has a wide range of applications in organisations, it still has certain limitations, of which we will learn about in this section. 1. Assumption of linear relationship 2. Constant value of objective and constraint equations 3. No scope for fractional value solutions 4. Degree of complexity 5. Unsuitab
Formulation of Linear Programming Model
The representation of an optimisation problem in a linear programming mathematical form is referred to as the formulation of an LP model. The basic steps in the formulation of an LP model are: 1. Identification of the decision variables 2. Identification of the constraints 3. Identification of the objective geektonight.com
|
Linear Programming
Most linear programs require that all decision variables be nonnegative. ASSUMPTIONS OF LINEAR PROGRAMMING MODELS. ? Sensitivity analysis allows the decision |
|
Integer Programming
The linear-programming models that have been discussed thus far all have been continuous in the sense that Often this is a realistic assumption. |
|
Nonlinear Programming
Linear programming assumptions or approximations may also lead to appropriate problem representations over the range of decision variables being considered. |
|
CHAPTER 11: BASIC LINEAR PROGRAMMING CONCEPTS
11-May-1998 A problem can be realistically represented as a linear program if the following assumptions hold: 1. The constraints and objective function are ... |
|
Duality in Linear Programming
These various correspondences are summarized in Table 4.1. The table is based on the assumption that the primal is a maximization problem. Since the dual of the |
|
Duality in Linear Programming
The payoff table in Tableau 12 and the conservative assumption on the player's behavior lead to the primal and dual linear programs discussed below. The column |
|
Fuzzy linear programming and applications
They mainly differ in the assumptions made in order to reduce the FLP to a classical mathematical optimization problem. In this paper we present a survey on |
|
Chapter 11 Dynamic Programming
Of the four assumptions of linear programming the only one needed by the distrib- ution of effort problem (or other dynamic programming problems) is |
|
Logistic and Linear Regression Assumptions: Violation Recognition
For Linear regression the assumptions that will be reviewed include: linearity |
|
Fuzzy linear programming and applications
They mainly differ in the assumptions made in order to reduce the FLP to a classical mathematical optimization problem. In this paper we present a survey on |
|
Linear Programming: Theory and Applications
11 mai 2008 · For instance, several assumptions are implicit in linear programing The example of a canonical linear programming problem from the |
|
LINEAR PROGRAMMING MODELS
A Linear programming problem can be expressed in the following standard form: max z= c1x1+ Assumptions of Linear Programming 1 Examples of LP |
|
BASIC LINEAR PROGRAMMING CONCEPTS - Faculty Washington
11 mai 1998 · Linear programming is a mathematical technique for finding optimal solutions to problems cases, where, for example, the variables might represent the levels of a set The Fundamental Assumptions of Linear Programming |
|
Linear Programming
tion Models B5 Assumptions of Linear Programming Models B6 The following example shows how an operational problem can be represented and analyzed |
|
LINEAR PROGRAMMING - ResearchGate
We now present examples of four general linear programming problems Under this assumption, the inequalities in constraints (2) and (3) must be satisfied |
|
LINEAR PROGRAMMING - NPTEL
example, let us assume that the revenue per table is 120 and revenue per chair is 70 define a Linear Programming problem, state the assumptions, introduce |
|
Introduction to Linear Programming
For example, the objective function coefficient for x1 is 3, and the objec- Does the Dorian model meet the four assumptions of linear programming outlined in |
|
101 Types of Constraints and Variables in Linear Programming
10 2 "Violations" of the Algorithmic Assumptions as well as LP assumptions 10 1 Types of Constraints and For example, a LP formulation of an automobile |
|
I Developing Linear and Integer Programming models
too many wild assumptions, in the form of an LP then you know you can get a The presentation below is given in terms of the following constraint types: |
|
Présentation PowerPoint
4 sept 2018 · Resolution based on Linear Programming – use case o Assumptions: 4 tramways, 1 sub-system per tramway for predictive maintenance |