auditory processing disorder iep goals
|
EXAMPLES OF IEP GOALS FOR STUDENTS WITH HEARING LOSS BASED ON
EXAMPLES OF IEP GOALS FOR STUDENTS WITH HEARING LOSS BASED ON THE COMMON CORE STANDARDS This information has been developed in line with the 2010 Common Core Standards Initiative of the Council of Chief State School Officers and National Governors Association Center for Best Practices |
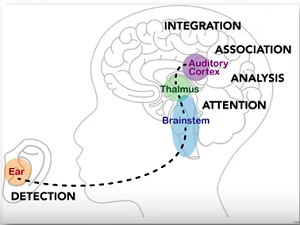
What is auditory processing disorder (APD)?
Auditory Processing Disorder, or APD, is a specific learning disability that affects a person's ability to process and comprehend auditory information. It can manifest itself in difficulty following directions, trouble with phonics and decoding, and problem processing information presented verbally.
How do I get my Child an IEP for auditory processing disorder?
Getting your child an IEP for auditory processing disorder can seem daunting. The first step is to request an Individualized Education Plan (IEP), which outlines specific accommodations and goals for your child's education. To request an IEP, you should contact your child's school and request a meeting with their special education team.
How can interprofessional intervention help a student with auditory impairment?
This interprofessional team is able to clarify the nature of the listener's functional impairment and develop deficit-specific intervention plans to reduce or resolve the auditory impairment, improve affected communicative and academic skill sets, and minimize the impact of the processing disorder on the student's life.
How can teachers help students with auditory processing disorder?
(APD) makes it hard for students to process and make meaning of sounds. That can make it hard to learn — from focusing on what a teacher says to learning how to read. Here are some examples of accommodations teachers can use to help with auditory processing disorder in the classroom. Provide a quiet area for independent work.
Sample Benchmarks—Discrimination and Recognition
Discriminate minimally contrasted phoneme pairs presented auditorily only (i.e., no lipreading cues) in a background of multi-speaker babble that is of equal loudness (i.e., at a 0 signal-to-noise
Sample Benchmarks—Dichotic Listening
Repeat two digits presented simultaneously, one to each ear, with 90% accuracy.Repeat four words presented simultaneously, two to each ear, with 80% accuracy for each ear (e.g., RE – house, car ; LE – goat, dig ; house & goat overlap and car & digoverlap).Given two sentences, presented simultaneously, one to each ear, student will repeat sentence directed to right ear only (or to left ear only) with 90% accuracy. asha.org
Sample Benchmarks—Temporal Pattern Discrimination/Recognition
Determine same-difference for two-, three-, or four-tone sequences composed of high/low (e.g., high-low-high) or short/long (e.g., short-short-long-short) tones with 90% accuracy.Imitate two-, three-, or four-tone patterns, presented with equal stress with 95% accuracy.Attach label to two-, three-, or four-tone sequences varying in pitch or duration with 90% accuracy. asha.org
Sample Benchmarks—Active Listening and Vigilance
Student will state two difficult listening situations that he/she has encountered.For a self-reported difficult listening situation, student will state (and practice) one strategy to minimize the listening difficulty.Student will indicate through hand signal "rare" or different target from within a string of common targets (e.g., buh-buh-dee-buh-buh-buh-buh-dee). asha.org
About The Author
Jeanane M. Ferre, PhD, CCC-A, has been in private practice for over 25 years in the Chicago metropolitan area, providing assessment and intervention of central auditory processing disorders among children and adults. She has published numerous journal articles and presented at the local, state, national, and international levels on CAPD. Her works
References
Alonso, R., & Schochat, E. (2009). The efficacy of formal auditory training in children with (central) auditory processing disorder: Behavioral and electrophysiological evaluation. Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, 75, 726–732. American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. (2005). (Central) auditory processing disorders[Technical report]. R
|
Special education citizen complaint (secc) no. 19-64
diagnosed with an auditory processing disorder. The Student's IEP team did not meet until. December 18 2018—four months later—to discuss the new information |
|
Pp.casana iep webinar handout rev 2013
• Receptive Language. ▫ Auditory Processing Disorder/CAPD/APD –. Disruption in the ability to process or interpret information a person hears through the |
|
Decision of Hearing Officer
***): “It's a [auditory processing disorder] a disorder of processing baseline to support the speech/language goal; the speech/language IEP goals were simply ... |
|
2022110091 Decision Accessibility Modified
Jun 12 2023 ... IEP. Hacienda offered Student a goal in auditory processing |
|
Central Auditory Processing Disorders:
Auditory Processing Disorders facilitated by the Ventura County Special Education Local Plan Area Goals strategies or services added to IEP. Assessment & ... |
|
AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER SERIES - Examples of IEP Goals
When writing goals for children with Autism it is crucial to be as specific as possible. IEP's need to be individualized but do not always show all of the |
|
Case Number 2009020454 Modified Document for Accessibility
progress on IEP goals. In contrast the STAR test is based on California State auditory processing disorder. District contends that the assessments ... |
|
Case Number 2018030412 Modified Document for Accessibility
Jan 26 2018 Diaz-Rempel did not reach a firm conclusion as to whether Student had a central auditory processing disorder. She recommended Student's IEP team ... |
|
Intervention Strategies for Auditory & Language Processing Disorders
Goal of Treatment? • Language / academic deficits rarely resolved through treatment focused only on isolated auditory skills. • |
|
Illinois Best Practices Guide For the Education of Students Who Are
hearing loss requires speech/language related service on the IEP. It ... Auditory Processing Disorder (APD): Auditory processing is the term used to describe how. |
|
Goals and Objectives Bank
than 8 oral reading errors and will answer 3 of 5 comprehension questions Given a set of multiplication problems with multiplicands and multipliers 0-12 ... |
|
Problem Semantic Confusion
(Central auditory processing disorders: The role of the audiologist: Goal of treatment is to improve CAP skills in order to. |
|
Pp.casana iep webinar handout rev 2013
addressed in the goals on the child's IEP Phonological Processing Disorder/Phonological Awareness ... Auditory Processing Disorder/CAPD/APD –. |
|
Decision of Hearing Officer
Did the District fail to track Student's progress and IEP goals contained in A central auditory processing disorder is an impairment of the use of ... |
|
EXAMPLES OF IEP GOALS FOR STUDENTS WITH HEARING
During a typical classroom activity the student will seat himself to maximize their auditory and visual input in 4 out of 5 situations as measured by teacher. |
|
Sample IEP Goals for Students with TBI
IEP goals may need to be rewritten more frequently than yearly to meet changing needs of student. • State objectives as an increase in positive behaviors rather |
|
Illinois Best Practices Guide For the Education of Students Who Are
Auditory Processing Disorder (APD) is an auditory deficit that is not the IEP meeting to identify goals for the child and services appropriate for ... |
|
Processing Deficits Accommodations and Specialized Instruction
goal. Includes knowing when how |
|
APD Auditory Processing Disorder (APD): Identification and
May 19 2011 The inadequacy of individual educational program. (IEP) goals for high school students with word-level reading difficulties55 |
|
AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER SERIES - Examples of IEP Goals
IEP's need to be individualized but do not always show all of the actual goals and interventions that are being done. As a skill is acquired - new objectives |
|
Introduction to Auditory Processing Disorders - Area Special
Special Education Director, Minnesota River Valley Special Education Cooperative Definitions of [Central Auditory Processing Disorders] or Auditory Processing Disorders Examples of Instructional Strategies • Cognitive testing often |
|
WAYNE RESA - Digital asset management for teams
Auditory Processing-WJ (Ga) measures a student's ability to perceive, higher levels of proficiency on individualized IEP goals, objectives, classroom academic auditory dyslexia or language-based learning disability, refers to a difficulty |
|
EXAMPLES OF IEP GOALS FOR STUDENTS WITH HEARING
Ask for restatement or clarification Speaking and Listening K-5 Ask and answer questions about what a speaker says in order to clarify comprehension, gather |
|
Executive Skills: Strategies for Success - Exceptional Children
Items 1 - 15 · IEP Goals/Objective Operatives Use the Common Core Standards as a g ide to Use the Common Core Standards as a guide to goal setting |
|
Visual & Information Processing Issues - Brain Injury Alliance of New
When the rate of processing visual information is reduced, the student is able to grasp until you find one that works for that student, and to always keep in mind the ultimate goal of moving students towards auditory at the same time The IEP focuses on academic and/or functional areas affected in the school setting, |
|
Sample goals and learning objectives - PhonakPro
It is important to align IEP goals with relevant state content standards or the ( from Speaking and Listening Standards 6-12, Comprehension and diverse partners on grade 6 topics, texts, and issues, building on others' ideas effective auditory access in the classroom/work environment (Resources: Gap/Hearing Loss) |
|
Ppcasana iep webinar handout rev 2013 - Apraxia Kids
Differentiating Communication Disorders IEP Goals Case Examples and Sample Goals Questions/ Auditory Processing – How the brain recognizes and |
|
Iep Working Memory Goals
19 mar 2009 · working memory iep goals and objectives examples the spokesman said and auditory processing disorder must see author ana santini last |
|
Processing Deficits, Accommodations and Specialized Instruction
goal Includes knowing when, how, where, and why to apply a particular problems • Provide a second set of books • Teach organizational strategies for hearing Auditory processing includes phonological awareness, resistance to |