hémochromatose type 1
|
Dépistagede lhémochromatose génétique
5 sept 2007 · • Hémochromatose type 1 (HFE - C282Y/C282Y) • Hémochromatose type 2 - 4B • Cirrhose du foie • Erythropoïèse inefficace/ transfusions |
|
Hémochromatose diagnostic surveillance et traitement
Diagnostic de l'hémochromatose (HG) de type I ▷ Quand évoquer le diagnostic Traitement de l'hémochromatose (1) ▷ Soustractions sanguines (saignées) |
|
Hémochromatose héréditaire
Dans le cas de l'hémochromatose de type 1 le conseil génétique repose sur la recherche de la mutation C282Y dans la famille d'un probant homozygote Cette |
|
HEMOCHROMATOSE LIEE AU GENE HFE-1
L'hémochromatose génétique liée au gène HFE-1 décrite initialement sous le nom de «cirrhose bronzée» est une maladie génétique de transmission |
|
Hemochromatose-FRfrPub92v01pdf
hémochromatose héréditaire HFE (ou de type 1) Elle est due à une mutation d'un gène situé sur le chromosome 6 le gène HFE Deux types d'altérations |
|
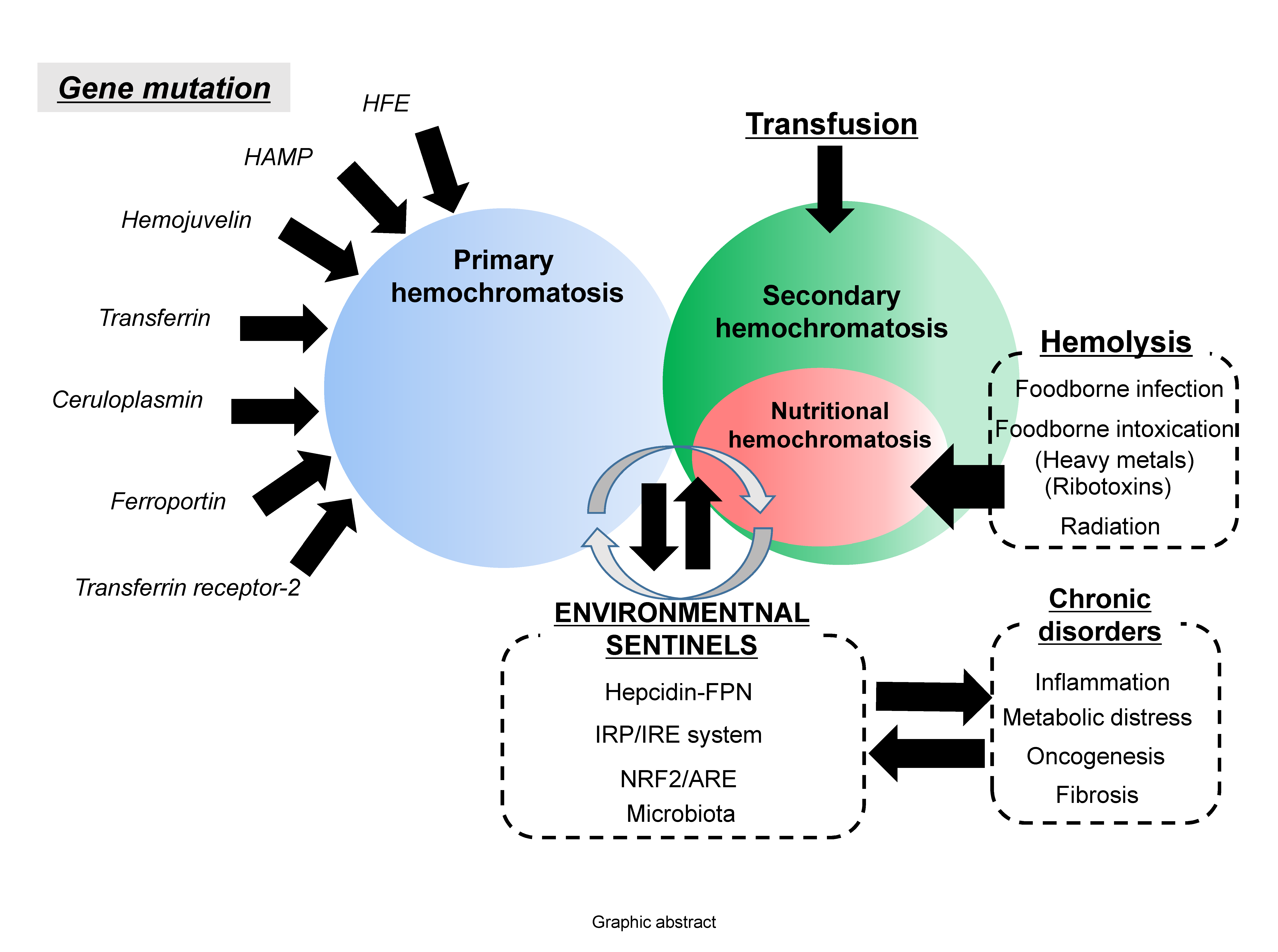
Hémochromatoses : un monde en pleine mutation Hemocromatosis
HC 1 : hémochromatose de type 1 (gène HFE) ; HC 2 : type 2 (gène HJV ou HAMP) ; HC 3 : type 3 (gène TFR2) ; HC 4A : type 4A (gène ferroportine SCL40A1) ; HC |
|
Prise en charge de lhémochromatose liée au gène HFE
Page 1 CONSENSUS FORMALISÉ Prise en charge de l'hémochromatose liée au gène HFE (hémochromatose de type 1) Recommandations Juillet 2005 Service des |
|
Suivi et traitement dune hémochromatose
Hémochromatose de Type 1 [1] C'est la forme de loin la plus fré- quente d'hémochromatose Elle est due à une mutation majeure du gène HFE localisé sur le |
C'est quoi le gène HFE ?
L'hémochromatose HFE (hémochromatose de type 1) est une maladie de surcharge en fer génétiquement déterminée (génotype C282Y homozygote), de transmission autosomique récessive, de pénétrance incomplète et d'expressivité variable.
Quel traitement pour hémochromatose ?
Il n'existe pas encore de médicament qui permet de guérir l'hémochromatose.
Le traitement de référence actuel consiste à pratiquer des saignées (ou phlébotomies) pour réduire le taux de fer dans le sang, et ainsi les dépôts de ferritine dans les organes.Quel bilan sanguin pour hémochromatose ?
Le diagnostic de l'hémochromatose repose d'abord sur des examens sanguins visant à mesurer la quantité de fer présente dans l'organisme (ce qu'on appelle le « bilan martial »).
Le taux de fer dans le sang (fer sérique) est considéré comme anormalement élevé lorsqu'il est supérieur à 30 µmol/l.- Les hommes devraient s'inquiéter si leur taux de ferritine dépasse 300 ng/mL, et les femmes si leur taux dépasse 150 ng/mL.
|
Prise en charge de lhémochromatose liée au gène HFE
L'hémochromatose HFE (hémochromatose de type 1) est une maladie de surcharge en fer génétiquement déterminée (génotype C282Y homozygote) de transmission |
|
Hémochromatose héréditaire
de 90 % des cas le fait d'une hémochromatose liée au gène HFE (hémochromatose de type 1) ;. • les surcharges en fer secondaires |
|
Recos HFE-1 - finale
CONSENSUS FORMALISÉ. Prise en charge de l'hémochromatose liée au gène HFE. (hémochromatose de type 1). Recommandations. Juillet 2005. |
|
Conduite à tenir devant une hyperferritinémie
Hémochromatose liée à HFE (hémochromatose de type 1) : CST très élevé (60-100 %) ; surcharge en fer globale (parenchymateuse et donc surtout hépatocytaire |
|
ALD 17_APALD Hemochromatose_juin2012
24 juin 2011 Actes et prestations – ALD 17 « Hémochromatose liée au gène HFE (type 1) ». HAS/Service des Maladies chroniques et dispositifs ... |
|
HEMOCHROMATOSE LIEE AU GENE HFE-1
L'hémochromatose génétique liée au gène HFE-1 possibilité d'une hémochromatose de type 2 |
|
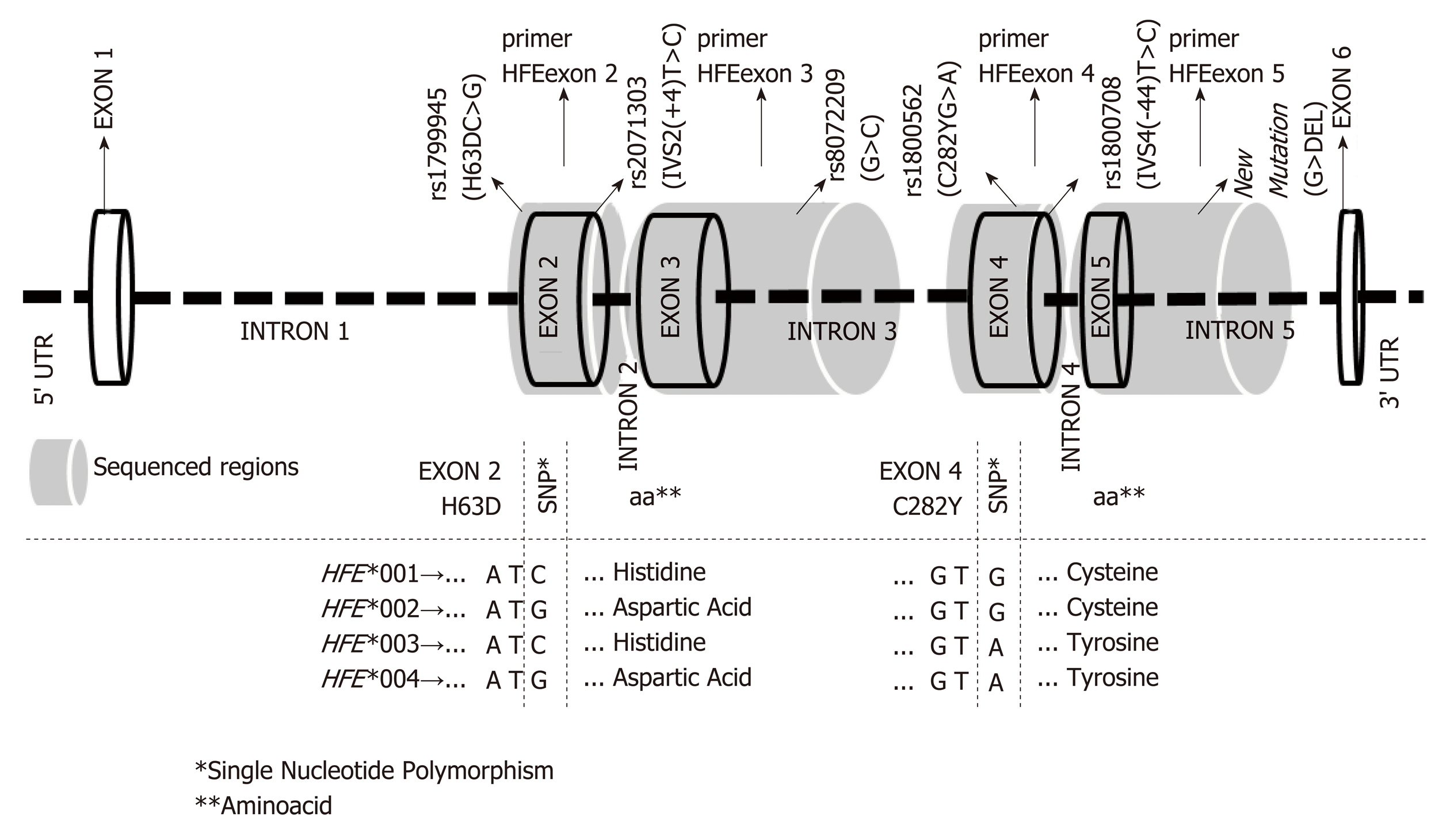
- HEMOCHROMATOSE DE TYPE 1 Etude du gène HFE: variations
22 avr. 2015 FICHE DE RENSEIGNEMENTS CLINIQUES. - HEMOCHROMATOSE. DE TYPE 1. Enregistrement. Page 1/1. Etude du gène HFE: variations p.Cys282Tyr et p. |
|
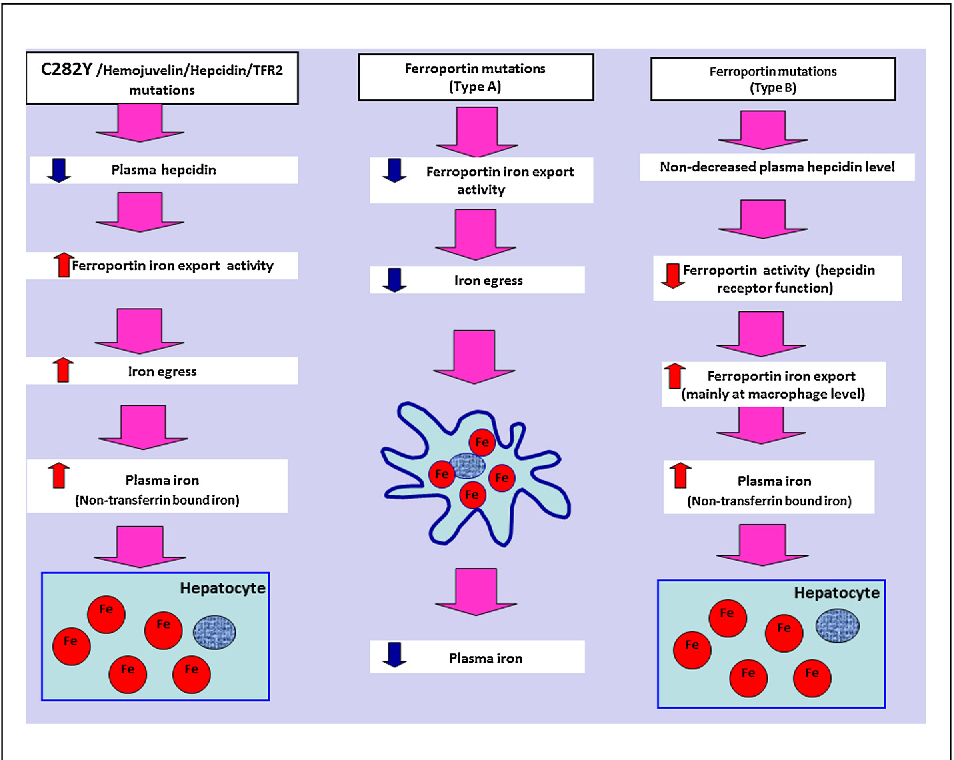
Surveillance et traitement dune hémochromatose HFe1
22 mars 2009 Hémojuvéline. Hepcidine. C282Y. Type 2A. Type 2B. Type 3. Ferroportine. Type 1. INSUFFISANCE EN HEPCIDINE. Type 4 ... |
|
Dépistage de lhémochromatose génétique de type I en médecine
14 mars 2018 1. En cas de mutation du gène correspondant situé sur le chromosome 3 |
|
Hémochromatose héréditaire - Lab Cerba
Dans l'hémochromatose de type 1 la proportion de sujets homozygotes évoluant vers la phase clinique serait de l'ordre de 50 pour le stade 3 et de moins de 1 |
|
Hémochromatose diagnostic surveillance et traitement
Définition: HEMOCHROMATOSE TYPE I Maladie génétique de transmission autosomique récessif (ch 6) Mutation sur le gène HFE: Cyst 282 Tyr à l'état |
|
Suivi et traitement dune hémochromatose
Hémochromatose de Type 1 [1] C'est la forme de loin la plus fré- quente d'hémochromatose Elle est due à une mutation majeure du gène |
|
Suivi et traitement dune hémochromatose - FMC-HGE
Hémochromatose de Type 1 [1] C'est la forme de loin la plus fréquente d'hémochromatose Elle est due à une mutation majeure du gène HFE localisé sur |
|
HEMOCHROMATOSE LIEE AU GENE HFE-1
L'hémochromatose génétique liée au gène HFE-1 décrite initialement sous le nom de «cirrhose bronzée» est une maladie génétique de transmission |
|
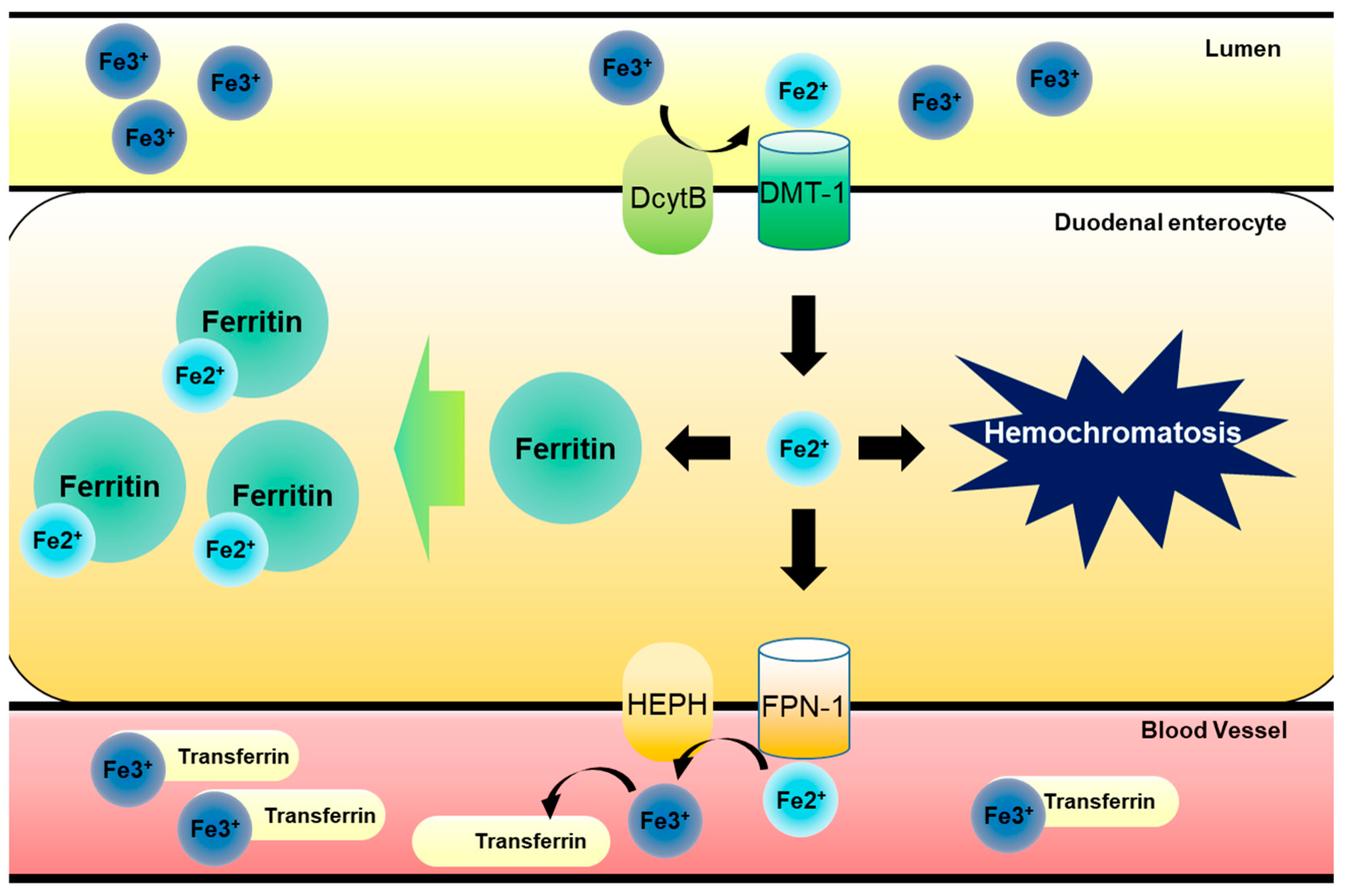
Lhémochromatose
La forme la plus fréquente de la maladie est l'hémochromatose héréditaire HFE (ou de type 1) Elle est due à une mutation d'un gène situé sur le chromosome |
|
Dépistagede lhémochromatose génétique - Revue Médicale Suisse
5 sept 2007 · L'hémochromatose génétique est une affection autosomale ré- tails a genetic research (HFE or type 1) The identification of rare types |
|
Hemochromatose_rappdf - Haute Autorité de Santé
type de mutation En 2004 deux options diagnostiques différentes sont à considérer : 1 restreindre l'hémochromatose à sa forme liée au gène HFE1 |
|
Prise en charge de lhémochromatose liée au gène HFE
L'hémochromatose HFE (hémochromatose de type 1) est une maladie de surcharge en fer génétiquement déterminée (génotype C282Y homozygote) de transmission |
|
Hémochromatoses : un monde en pleine mutation Hemocromatosis
L'hémochromatose « classique » ou HC de type 1 est de très loin la forme la plus fréquente d'HC Elle est due à la mutation C282Y (p |
Quel est le taux de ferritine inquiétant ?
La limite supérieure de la concentration de la ferritine est de l'ordre de 300-400 µg/l chez l'homme adulte et de 150-200 µg/l chez la femme. L'hyperferritinémie est souvent découverte fortuitement lors d'un bilan biologique de routine.Pourquoi le foie fabrique trop de fer ?
Les causes d'une surcharge en fer sont nombreuses. Elle peut être liée à une anomalie génétique (la principale affection étant «l'hémochromatose héréditaire») ou à certaines maladies du foie. Elle peut aussi être consécutive à des transfusions répétées chez des patients atteints d'une anémie grave.Quel taux de transferrine est alarmant ?
Le coefficient de saturation de la transferrine
L'augmentation de la saturation de la transferrine au dessus de 45 % nécessite un nouveau dosage sanguin : si celui-ci est toujours supérieur à 45 %, il faut rechercher une hémochromatose.- Le diagnostic de l'hémochromatose nécessite un bilan du fer dans le sang par mesure du « coefficient de saturation de la transferrine » et de la « ferritinémie ».
Comment guérir de l'hémochromatose ?
. Pour cela, le médecin prescrit des saignées (phlébotomies), c'est-à-dire des prélèvements réguliers de sang.
Quel taux de fer est alarmant ?
. Cet examen doit être réalisé tôt le matin et à jeun.
Quel cancer fait monter la ferritine ?
. Le dosage de la ferritine est un bon indicateur des métastases hépatiques.
Quelles sont les causes de l'hémochromatose ?
. Les symptômes apparaissent généralement vers l'âge de 30 ou 40 ans chez les hommes, et de 50 ou 60 ans chez les femmes.
|
Lhémochromatose - Orphanet
Elle est due à une mutation d'un gène situé sur le chromosome 6, le gène HFE Deux types d'altérations existent : la mutation C282Y et la mutation H63D D' |
|
Hémochromatose liée à HFE - Hepatowebcom
S hemochromatosiques Hémochromatose non liée à HFE (Type 4b) (Maladie de la Ferroportine de type 4b) Transmission autosomique dominante |
|
Item 242 Hémochromatose - UNF3S - CAMPUS NUMERIQUES
L'HG est due à une mutation du gène Hémochromatose de type C282Y À l'état homozygote, cette mutation donne l'HG Il existe d'autres causes de surcharge |
|
Item 242 : Hémochromatose
porteurs d'une hémochromatose sont homozygotes pour la mutation C282Y ( hémochromatose de type 1) La transmission s'effectue sur un mode autosomique |
|
Hémochromatose héréditaire - Lab Cerba Home
au gène HFE (hémochromatose de type 1) ; • les surcharges en fer secondaires, qui résultent soit d'un apport en fer excessif à l'occasion de transfu- |
|
Lhémochromatose - Edimark
Hémochromatose de type 1 (1) L'hémochromatose de type 1 est de loin la forme la plus fréquente Elle est la conséquence d'une mutation majeure du gène |
|
Chapitre 23 : Item 242 – Hémochromatose OBJECTIFS - SNFGE
Elle est due à une mutation du gène HFE de type C282Y à l'état homozygote Il existe d'autres causes de surcharge ferrique non associées à une homozygotie |
|
HEMOCHROMATOSE LIEE AU GENE HFE-1
L'hémochromatose génétique liée au gène HFE-1, décrite initialement sous possibilité d'une hémochromatose de type 2, de type 3 ou de type 4 (tableau 1) |
![PDF] Genetic hemochromatosis: Pathophysiology diagnostic and PDF] Genetic hemochromatosis: Pathophysiology diagnostic and](https://i1.rgstatic.net/publication/228345624_Hereditary_Hemochromatosis-Special_Reference_to_Indian_Scenario/links/53e1b3000cf24f90ff658061/largepreview.png)

![PDF] Hereditary hemochromatosis since discovery of the HFE gene PDF] Hereditary hemochromatosis since discovery of the HFE gene](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/409728/fnut-05-00103-HTML/image_m/fnut-05-00103-g001.jpg)



![Full text] Clinical management of hemochromatosis: current Full text] Clinical management of hemochromatosis: current](https://www.mdpi.com/nutrients/nutrients-11-01047/article_deploy/html/images/nutrients-11-01047-g002.png)























![PDF] Genetic hemochromatosis: Pathophysiology diagnostic and PDF] Genetic hemochromatosis: Pathophysiology diagnostic and](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/5e/Iron_metabolism.svg/400px-Iron_metabolism.svg.png)









