atrial septal defect pediatric pdf
|
Atrial Septal Defect Guideline
Introduction Atrial septal defects (ASDs) are holes in the atrial septum and account for 7-10 of all congenital heart defects (CHD) 3rd most common defect There is a higher incidence in females (Kazmouz 2013) ASDs are also part of many of the more complex forms of congenital heart disease |
Should a child close an atrial septal defect?
The decision to close the ASD may also depend on the size of the defect. Individuals who have their atrial septal defects repaired in childhood can prevent problems later in life. Many children have no symptoms and require no medications.
Do girls have atrial septal defects?
Atrial septal defects occur in a small percentage of children born with congenital heart disease. For unknown reasons, girls have atrial septal defects twice as often as boys. Our team is standing by to schedule your child’s appointment. This animation presents the anatomy of the heart in detail.
What is an atrial septal defect (ASD)?
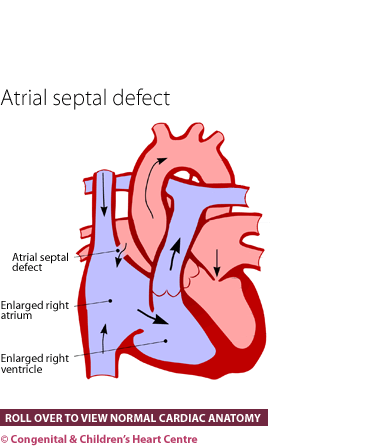
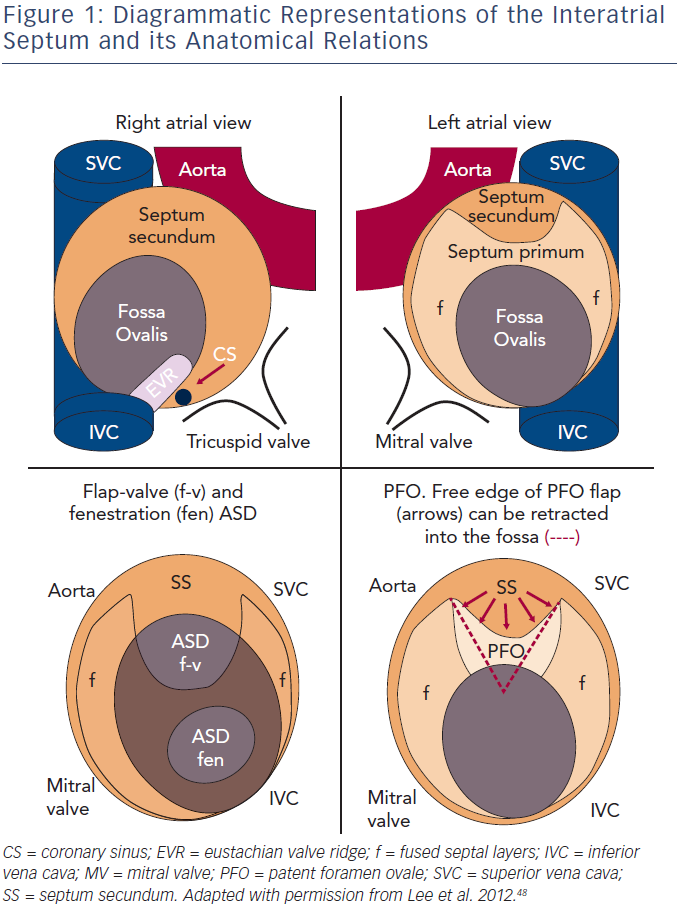
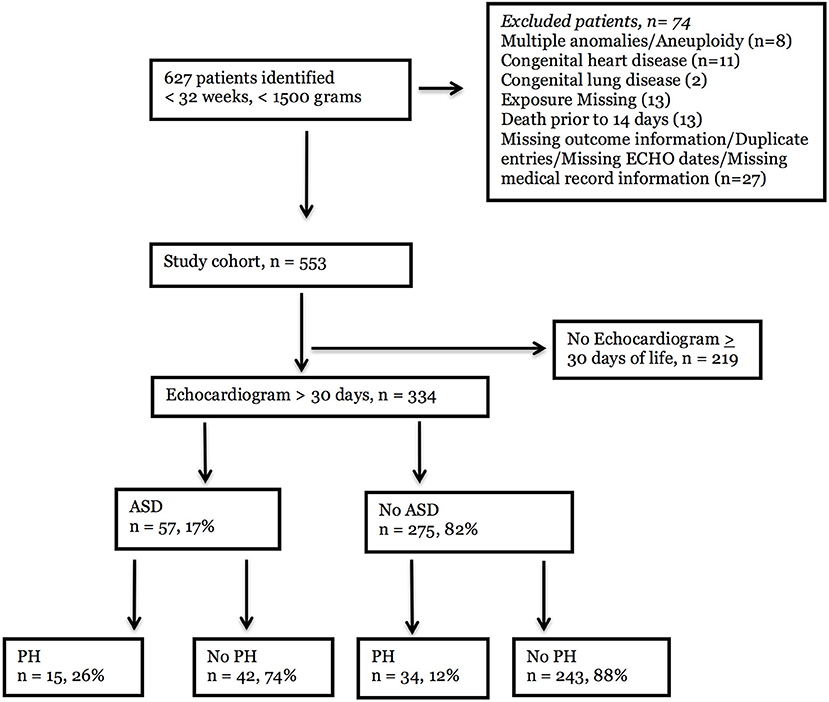
An atrial septal defect (ASD) is an opening in the interatrial septum, causing a left-to-right shunt and volume overload of the right atrium and right ventricle. Children are rarely symptomatic, but long-term complications after 20 years of age include pulmonary hypertension, heart failure, paradoxical emboli, and atrial arrhythmias.
What Is An Atrial Septal Defect in Children?
The atrial septum is the wall between the 2 upper chambers of the heart (right and left atria). An atrial septal defect (ASD) is an abnormal hole in this wall. ASD is a heart problem that is present at birth (congenital). ASDs can happen on their own. Or they can happen in children born with other congenital heart defects. Girls have ASDs twice as
What Causes An Atrial Septal Defect in A Child?
The heart forms during the first 8 weeks of pregnancy. It starts as a hollow tube and divides into 4 chambers. These chambers are separated by walls (septa). It's normal for the walls to have openings as the fetus grows. The openings usually close shortly before or just after birth. If they don't all close, the atrial septum will have a hole in it
What Are The Symptoms of An Atrial Septal Defect in A Child?
Many children have no symptoms and seem healthy. If the ASD is large, your child may have symptoms. Your child may: 1. Tire easily 2. Have fast breathing 3. Have shortness of breath 4. Grow slowly 5. Have respiratory infections often 6. Have abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmias) Older children and adults with ASDs may have migraine headaches. But it'
How Is An Atrial Septal Defect Diagnosed in A Child?
Your child's healthcare provider may have heard a heart murmur when listening to your child's heart with a stethoscope. The heart murmur is from the abnormal flow of blood through the heart. Your child may need to see a pediatric cardiologist for a diagnosis. This is a doctor with special training in treating heart problems in children. The doctor
How Is An Atrial Septal Defect Treated in A Child?
Treatment will depend on your child’s symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is. The most common type of ASD may close on its own as your child grows. Once an ASD is diagnosed, your child's cardiologist will check your child to see if the defect is closing on its own. An ASD will usually be fixed if it ha
What Are Possible Complications of An Atrial Septal Defect in A Child?
Large ASDs may cause lung problems over time if not treated. This is because the extra blood passing through the defect and then into the lungs may harm the vessels in the lungs. stanfordchildrens.org
How Can I Help My Child Live with An Atrial Septal Defect?
All children with an ASD need to be cared for by a pediatric cardiologist. Most children who have had an ASD repair will live healthy lives. After the repair, your child's doctor may want your child to take antibiotics. This will prevent an infection of the heart lining (bacterial endocarditis). With early diagnosis and repair of an ASD, children u
When Should I Call My Child's Healthcare Provider?
Call your child's healthcare provider if your child has new symptoms or symptoms that get worse. Symptoms may include: 1. Tiredness that gets worse 2. Troubled breathing 3. Fast breathing 4. Racing or fluttering heartbeat (palpitations) 5. Poor feeding stanfordchildrens.org
Key Points About Atrial Septal Defect in Children
An ASD is an opening in the wall dividing the 2 upper chambers of the heart.Symptoms of an atrial septum defect include tiring easily, fast breathing, shortness of breath, poor growth, arrhythmias, and frequent respiratory infections.Atrial septum defects range from small to large.Small atrial septum defects may close on their own. stanfordchildrens.org
Next Steps
Tips to help you get the most from a visit to your child’s healthcare provider: 1. Know the reason for the visit and what you want to happen. 2. Before your visit, write down questions you want answered. 3. At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis, and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. Also write down any new instructions your pr

Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) Nursing Congenital Heart Defects Pediatrics NCLEX

ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT (ASD) Causes Signs and Symptoms Diagnosis and Treatment.

s=
|
Atrial Septal Defects in Children - An Angiocardiographic Study
D EFECTS in the atrial septum are of relatively great clinical importance. They are the most common of all congenital cardiac malformations constituting. |
|
Incidence of atrial septal defects in children attended the Cardiac
12 févr. 2020 3Department of Pediatrics Cardiology Cardiac Center of Ethiopia |
|
Minimally Invasive Pediatric Cardiac Surgery. Atrial Septal Defect
16 févr. 2011 In a previous study9 we compared midline sternotomies and right anterolateral (submammary) approaches for atrial septal defect (ASD) closure ... |
|
Understanding your childs heart Atrial septal defect
This factsheet is for the parents of babies and children who have an atrial septal defect (ASD). It explains. • what an atrial septal defect is and how it |
|
Young children with atrial septal defect
ISBN: 978-91-7855-281-8 (pdf) atrial septal defects in preterm children ... Incidence of atrial septal defect among preterm children and independent. |
|
Prognosis for Pediatric Patients with Isolated Atrial Septal Defect
Background: Atrial septal defect (ASD) is the second most frequently seen type of congenital heart incidence rate of ASD in children varies among au-. |
|
Transcatheter Atrial Septal Defect Device Closure - A 2.5 Years
transcatheter device closure of secundum atrial septal defect at the Pediatric Cardiology Unit Assiut University Children. Hospital. |
|
Atrial septal defect (ASD)
The atrial septum is the wall of tissue and atrial septal defect? Children with an atrial septal defect (or ... septal defect factsheet (PDF). |
|
Clinic al Pathway: Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) or Atrial Septal
Clinic al Pathway: Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) or. Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) Repair o MUF: neonate circuit; available with pediatric circuit. |
|
Atrial septal defect in adulthood: a new paradigm for congenital
25 juil. 2022 Surgery Masonic Children's Hospital |
|
Atrial septal defects - CORE
9 avr 2014 · outcomes of atrial septal defects in children and adult patients in whom this defect is the primary cardiac anomaly Introduction Atrial septal defects belong to a group of congenital cardiac pdf (accessed Feb 7, 2014) |
|
ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT IN CHILDREN - BMJ Heart
This paper has a two-fold purpose: first, to present the signs and symptoms of atrial septal defect and thus outline the findings that help in making the clinical |
|
Atrial septal defect - Great Ormond Street Hospital
The atrial septum is the wall of tissue and muscle between the Children with an atrial septal defect (or PFO) may only septal defect factsheet (PDF) ▫ Read |
|
Understanding your childs heart Atrial septal defect - British Heart
This factsheet is for the parents of babies and children who have an atrial septal defect (ASD) It explains, • what an atrial septal defect is and how it is diagnosed • |
|
A Atrial Septal Defect - The Royal Childrens Hospital
incisions for different types of defects o closure techniques (direct suture vs patch ) o treatment of associated anomalies (e g , Atrial Septal defect, right ventricular |
|
Incidence of atrial septal defects in children attended the - bioRxiv
12 fév 2020 · 42 incidence and patterns of spontaneous and surgical closure of ASD and their outcomes 43 44 Keywords: Congenital heart defect, Atrial |
|
Predictors of Spontaneous Closure of Isolated Secundum Atrial
CONCLUSIONS In the present study population of children with atrial septal defects, 62 showed spontaneous closure (34 ) or regression to 3 mm ( |
|
Ventricular and Atrial Septal Defects - Pediatrics in Review
Review the anatomy of ventricular septal defect (VSD) and atrial septal defect ( ASD) 2 Describe the clinical variables in children who have VSD and ASD 3 |