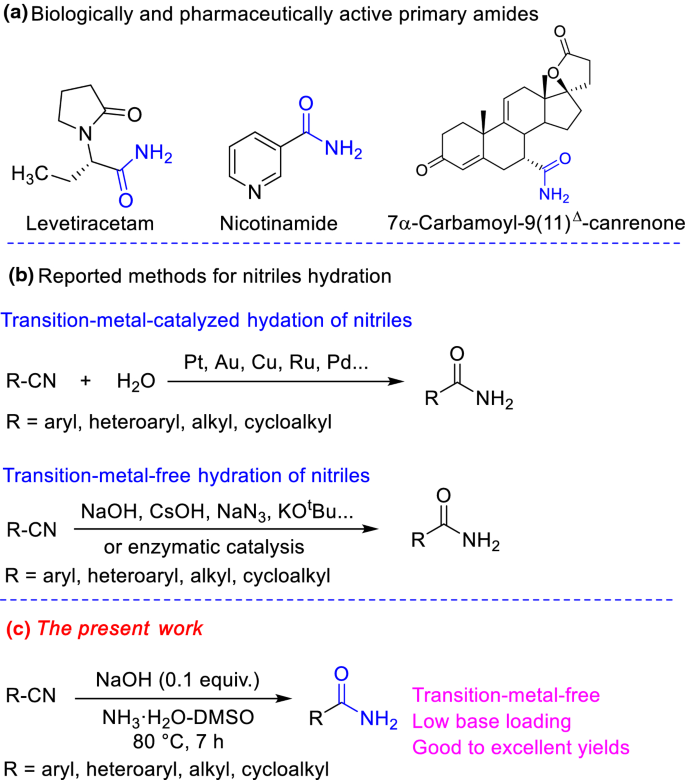
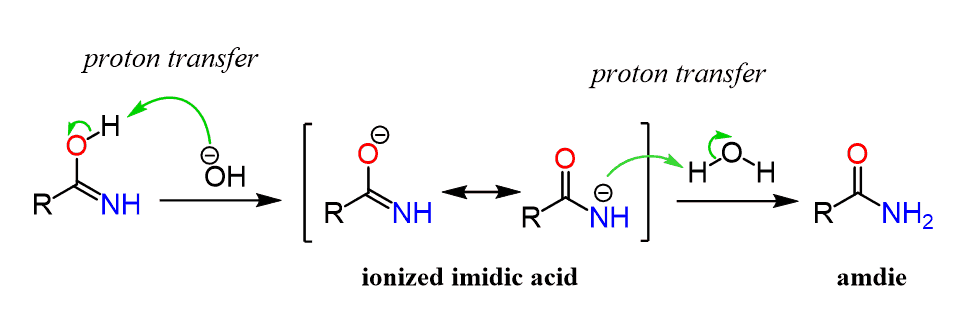
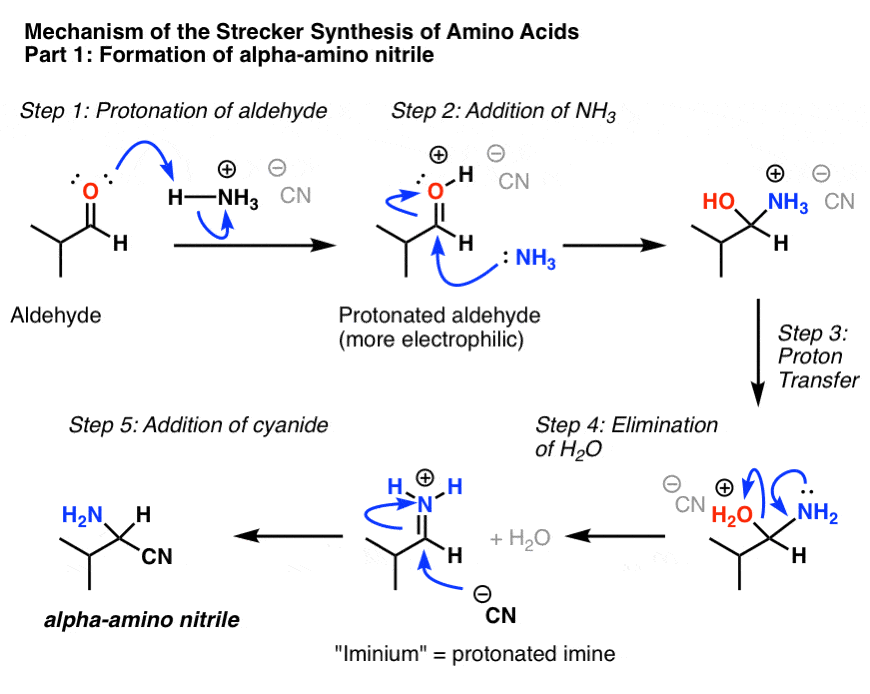
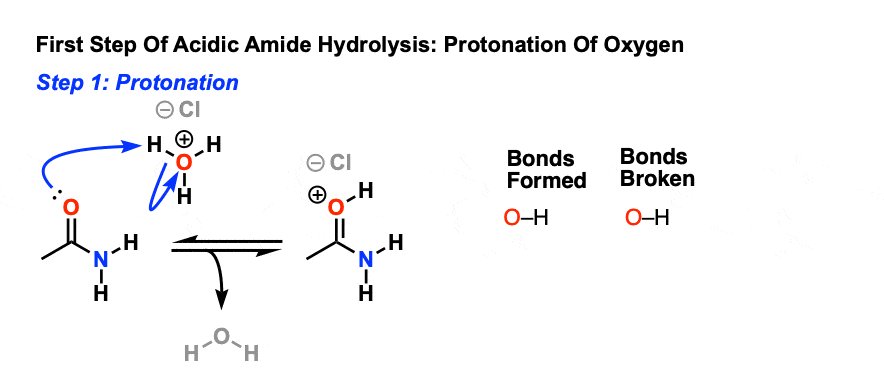
acid catalyzed hydrolysis of nitriles mechanism
What is the mechanism of acid hydrolysis of nitrile?
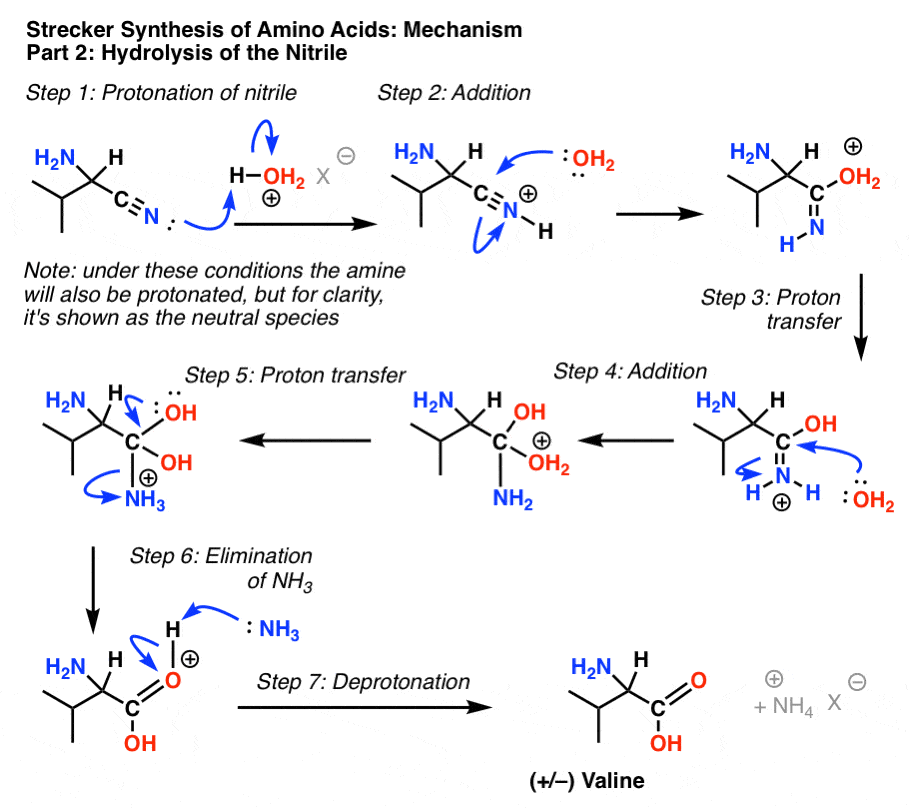
What happens when nitriles undergo acid hydrolysis? Under acidic conditions, instead of getting an ammonium salt, carboxylic acid is formed.
For example, Ethanenitrile on getting hydrolysed in hydrochloric acid gives ethanamide in the first step, while ethanoic acid and ammonium chloride in the second step.What is the mechanism of nitrile carboxylic acid?
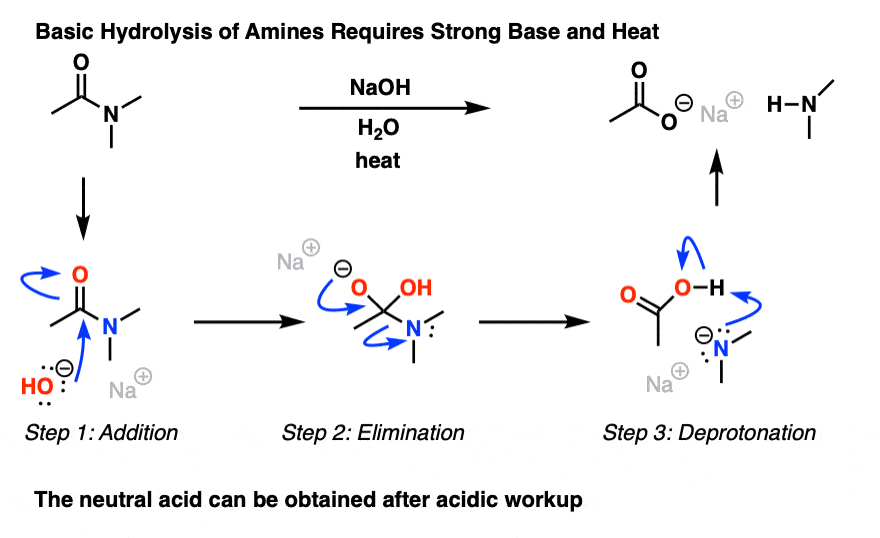
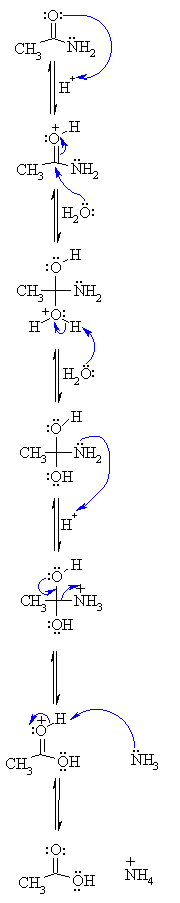
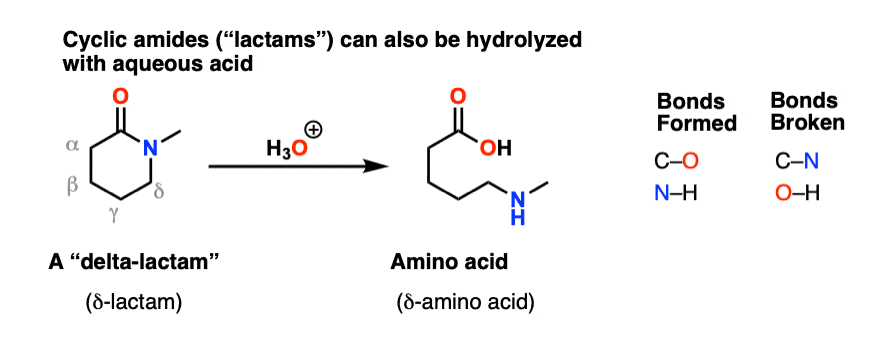
Nitriles can be hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids in acidic aqueous solutions, and to carboxylate salts with base-catalyzed hydrolysis: In both cases, the transformation consists of two main parts; conversion of the nitrile to an amide and hydrolysis of the amide to the corresponding carboxylic acid.
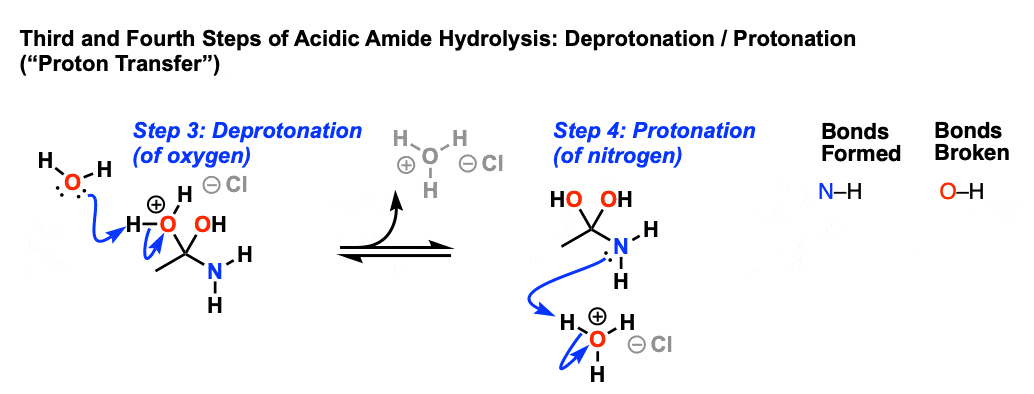
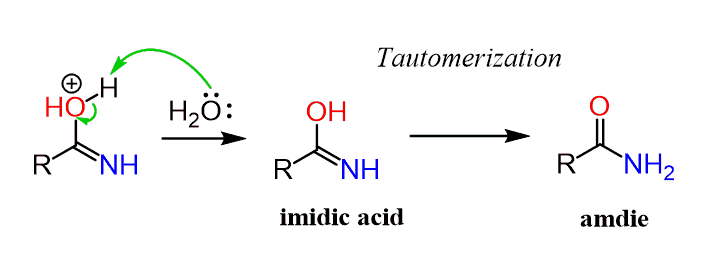
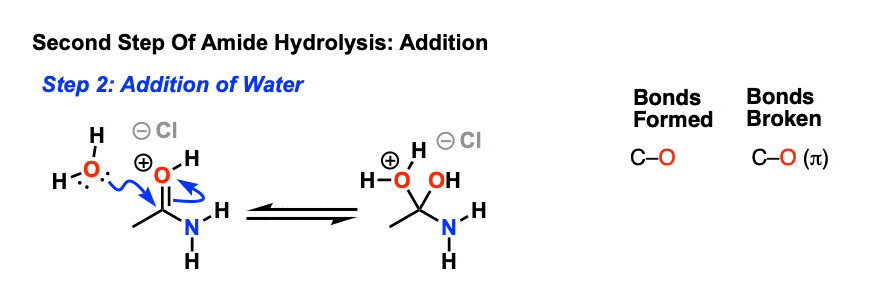
The first step in acid-catalyzed amide hydrolysis is the protonation of the carbonyl oxygen atom of the amide group.
The rate-determining step is the nucleophilic attack of a water molecule to the carbon atom of the amide group.
During this process one proton is transferred to the water phase.
|
Mechanism of the Acid-catalyzed Hydrolysis of Reissert Compounds
In an acid-catalyzed hydrolysis reaction permitted to go only to 25% of completionl-benzoyl-1 potassium cyanide or hydrogen cyanide in a variety. |
|
Scope and mechanism of the reaction of alkylidenephosphoranes
In reactions of both aliphatic and aromatic nitriles with ylides derived acid-catalyzed hydrolysis afforded desoxybenzoin and. |
|
21.7 HYDROLYSIS OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
acid-catalyzed hydrolysis is the exact reverse of the mechanism of Nitriles are hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids and ammonia by heating them in strongly ... |
|
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
mechanism it is possible to transform one acid The reactivity of acid derivatives can be correlated ... Base Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Nitriles. |
|
Chem 360 Jasperse Ch. 20 21 Notes + Answers. Carboxylic Acids
via Formation and Hydrolysis of Nitriles (Reaction 6) b) “Lateral” hydrolysis: From esters with water and acid catalysis (ACID WATER). • mechanism ... |
|
HYDROLYSIS 2016.pdf
Hydrolysis reactions are generally enhanced by both acids and bases and three Epoxides undergo hydrolysis by neutral and acid catalyzed mechanisms under ... |
|
Direct Synthesis of Nitriles from Carboxylic Acids Using Indium
18 sept. 2019 then dehydrated into the corresponding nitrile E such dehydration is promoted through imide C hydrolysis. The reverse mechanism can also be ... |
|
Chapter 1 Introduction
2.3 Introduction to nitrile hydrolysis. 22. 2.3.1 Classical methods—strong acid or base. 23. 2.3.2 Enzymatic methods. 27. 2.3.3 Catalysis with transition |
|
Tipping the Scales€â•Â€Specifier Proteins in Glucosinolate
stretching about 200 amino acids each. Myrosinase-catalyzed hydrolysis of glucosinolates in the presence of NSP leads to the formation of simple nitriles |
|
Chemistry 204: Carboxylic Acids and their Derivatives
mechanism of acid hydrolysis: 1) base and acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of nitriles ... alternate mechanism 1 (t-butyl benzyl esters; acid catalysis). |
|
217 HYDROLYSIS OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
First, in acid-catalyzed hydrolysis, the carbonyl carbon can react with the relatively weak nucleophile water because the carbonyl oxygen is protonated Specifically, the mechanisms of these reactions are classified as nucleophilic acyl substitu- tion mechanisms |
|
Theoretical study of nitrile hydrolysis by solid acid catalysts
1 jan 2000 · Subject headings: reaction mechanism; hydrolysis/ nitrile/ quantum of enols (9) are few examples of the application of acid catalysis Lately |
|
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
acid ester anhydride acyl halides amides compounds with groups that can be replaced The general mechanism of this Acid Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Amides |
|
Lecture 6: Hydrolysis Reactions of Esters and Amides
form new esters by base- or acid-catalysed transesterification mechanisms; draw the mechanism of hydrolysis of amides under acidic and basic reaction |