explain why aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reaction
|
Carbonyl Chemistry (12 Lectures) Aldehydes and Ketones
nucleophilic addition to carbonyl compounds; however other nucleophiles can undergo the same reaction. • There are other acid- and base-catalyzed examples. |
|
Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Aldehydes
Since aldehydes and ketones both possess the carbonyl functional group they undergo similar chemical reactions. 1. Nucleophilic addition reactions. |
|
Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Carboxylic Acids
Since aldehydes and ketones both possess the carbonyl functional group they undergo similar chemical reactions. 1. Nucleophilic addition reactions. |
|
16: Addition and Substitution Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds
Reaction of Amines with Ketones or Aldehydes (16.5A). Ammonia or 1° and 2° amines |
|
Unprecedented Diastereoselective Addition Reactions of 66
plexes undergo nucleophilic addition with the generation of one or two new stereocenters. Reactions Coupling Reactions of 1 with Aldehydes and Ketones". |
|
SCH 206
Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reactions with amines to initially form carbinolamines. The carbinolamine intermediate is unstable and |
|
Reactions of Ketones and Aldehydes Nucleophilic Addition
The most characteristic reaction of aldehydes and ketones is nucleophilic addition to the carbon– Aldehydes and ketones undergo a reversible reaction ... |
|
Organic Chemistry
14 mars 2019 How Aldehydes and Ketones React? Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition–elimination reactions with nucleophiles that have a lone ... |
|
Your search term is: aromatic primary diamine synthesis
carbonyl group and the presence of the weak ? bond explain much of the Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reactions whereas. |
|
12 ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes that have no ? -hydrogen atoms undergo Cannizzaro's reaction. |
|
Reactions of Ketones and Aldehydes Nucleophilic Addition
The most characteristic reaction of aldehydes and ketones is nucleophilic addition to the carbon– Aldehydes and ketones undergo a reversible reaction |
|
Chapter 19 Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
Aldehydes and ketones are characterized by the carbonyl functional group (C=O) The compounds occur widely in nature as intermediates in |
|
194: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
24 sept 2022 · explain why in general aldehydes undergo nucleophilic addition reactions more readily than do ketones and determine which of two given |
|
Nucleophilic Addition Reaction - General Mechanism Examples
26 juil 2020 · Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reactions with monohydric alcohols to yield hemiacetals Upon further reaction with |
|
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
For that the first converting the keto group to an acetal then reducing the ester with LiAlH4and then removing the acetal by treatment with aqueous acid |
|
Carbonyl Chemistry (12 Lectures) Aldehydes and Ketones
Carbonyl groups in aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reactions nucleophilic addition to carbonyl compounds; however other nucleophiles can |
|
Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Carboxylic Acids
Since aldehydes and ketones both possess the carbonyl functional group they undergo similar chemical reactions 1 Nucleophilic addition reactions |
|
J3 NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION - Organic Chemistry Second Edition
Reaction of aldehydes and ketones with HCN and KCN produce cyano- hydrins The cyanide ion is the nucleophile and adds to the electrophilic carbonyl carbon The |
|
Nucleophilic Addition Reaction: Types Mechanism Examples and
Aldehydes are more reactive and readily undergo nucleophilic addition reactions in comparison to ketones Aldehydes demonstrate more favourable equilibrium |
|
Nucleophilic Addition To Carbonyls - Master Organic Chemistry
9 sept 2022 · For example aldehydes and ketones undergo addition with cyanide ion to give cyanohydrins |
Why aldehyde and ketone undergo nucleophilic addition reaction?
Due to greater electronegativity of oxygen than carbon, the C atom of the C=O. group acquires a partial positive charge in aldehydes and ketones and hence readily undergo nucleophilic addition reactions.Why aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition while alkenes undergo electrophilic addition?
Answer: Alkenes undergo electrophilic addition, whereas aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition because, in alkenes, the double bond joins two carbon atoms, and there is no resultant polarity. While in carbonyl compounds, the double bond joins atoms having different polarities.Does aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reaction?
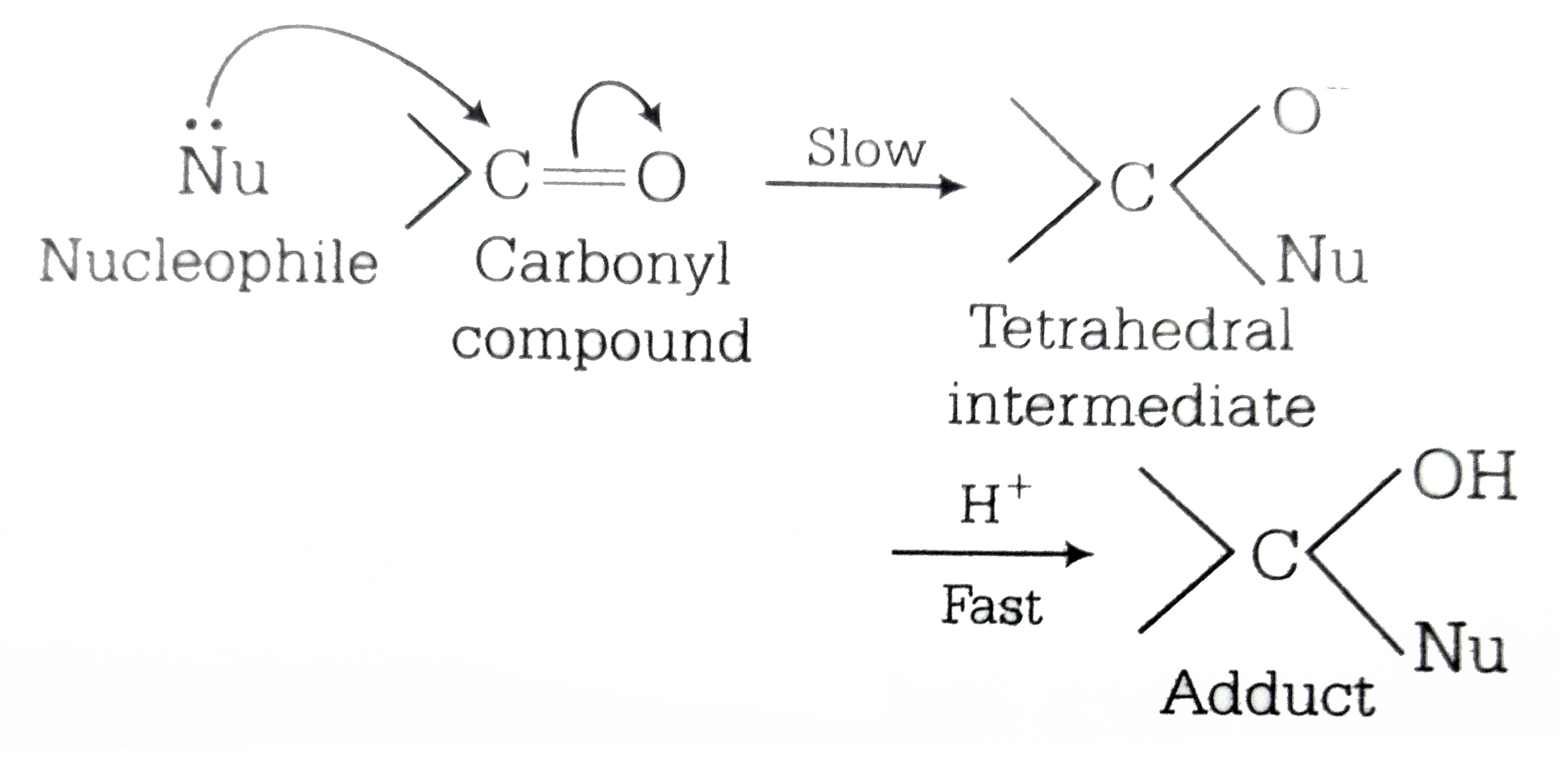
Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reactions, which is a reaction that occurs since the oxygen atom now has a negative charge, it can pick up a hydrogen ion from solution, forming alcohol on the carbonyl carbon.- Because the carbonyl carbon of aldehydes and ketones do not contain suitable leaving groups, their primary reaction is fundamentally different than carboxylic acid derivatives. Remember that aldehydes and ketones tend to undergo nucleophilic addition to form a tetrahedral alkoxide intermediate.
|
Carbonyl Chemistry (12 Lectures) Aldehydes and Ketones - chicac
– Both Bronsted and Lewis acids can interact with a lone pair of electrons on the carbonyl oxygen Addition Reactions – Carbonyl groups in aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reactions Carbonyl groups in aldehydes and ketones may be oxidized to form compounds at the next “oxidation level”, that of carboxylic acids |
|
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Based on 19 1 Naming Aldehydes and Ketones ▫ Aldehydes are named by replacing the terminal -e of Alkenes with a vinylic hydrogen can undergo oxidative The general reaction pathways of Nucleophilic Addition The reaction yields a pure alkene of defined structure |
|
Reactions of Ketones and Aldehydes Nucleophilic Addition
ketones is nucleophilic addition to the carbon– Reaction of Organometallic Reagents with Aldehydes as the hydrate in water but 2- hydroxyethanal does not exist as its hemiacetal Explain Aldehydes and ketones undergo a reversible |
|
Nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl group
Molecular orbitals explain the reactivity of the carbonyl group The carbonyl group, as found in aldehydes, ketones, and many The reaction has two steps: nucleophilic addition of cyanide, followed by protonation of the not free to undergo reaction, the nitrogen atom always lay on or near the 107° trajectory described |
|
16: Addition and Substitution Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds
of Carbonyl Compounds 16 1 Carbonyl Groups React with Nucleophiles 16-4 Acid Catalyzed Addition of HOH to Aldehydes and Ketones (16 3B) 16-11 in nucleophilic addition reactions and we describe some of them later in this chapter Carboxylic acids undergo an acid-base reaction with NH3 or amines to form |
|
UNIT 6 NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION TO CARBONYL COMPOUNDS
In this unit we shall discuss the nucleophilic addition reactions'of aldehydes and ketones explain the relative reactivity of aldehydes and ketones, discuss the indairun loas, which undergo further reaction to give enamines (vinylamines) ? |
|
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - NCERT
Unit 13, Class XI), the aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition nucleophilic addition reactions due to steric and electronic reasons Sterically, the |
|
Organic Chemistry II
15 sept 2019 · Carbonyl Compounds; Aldehydes and Ketones (i) Mechanism of Nucleophilic Addition Reactions electronic reasons Aldehydes and ketones having at least one α-hydrogen undergo a reaction in the presence of dilute |
|
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS ALDEHYDES AND - Caltech Authors
Especially important are the addition reactions of carbonyl groups, and this chapter is for other carbonyl compounds (see Table 16-I)? Explain why the dipole moment of CO is very Thus compounds such as the following add nucleophilic reagents readily: tion-reduction they undergo in the presence of strong base |
|
Ketones and Aldehydes
explain the dipole moment It is this polarization that The most common reaction of aldehydes and ketones is nucleophilic addition Carbonyl compounds undergo reaction with nucleophiles because of the polarization of the C=O bond |














![12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic acids - [PDF Document] 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic acids - [PDF Document]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e1/Typical_aldol-en.svg/600px-Typical_aldol-en.svg.png)