alkene br2
Which reaction occurs easily between halogens and alkenes?
Addition reaction also occur easily between halogens (Br 2 and Cl 2) and alkenes. In the presence of aprotic solvent, the product is a vicinal dihalide, as shown here for the addition of chlorine to propene. The reaction between C=C double bond and bromine (Br 2) can be used as a test for the presence of alkene in an unknown sample.
Is a second molecule of Br2 a termolecular mechanism?
In some solvents it turns out to be energetically favorable for a second molecule of Br 2 to be involved in bonding to the Br- that is expelled in the process (yes, a “termolecular” mechanism). For more details see here (J. Phys Chem A, 2007, 111, 13218)
How does an alkene attack a bromine atom?
The alkene donate a pair of π electrons to the closer bromine, causing the displacement of the bromine atom that is further away. The lone pair on the closer bromine atom then acts as nucleophile to attack the other sp 2 carbon.
How do you test for alkene in a vicinal dibromide reagent?
The reaction between C=C double bond and bromine (Br 2) can be used as a test for the presence of alkene in an unknown sample. The bromine reagent is in reddish color, and the product vicinal dibromide is colorless. When bromine is added to the sample, if the reddish color disappear, that means the sample does contain an alkene.
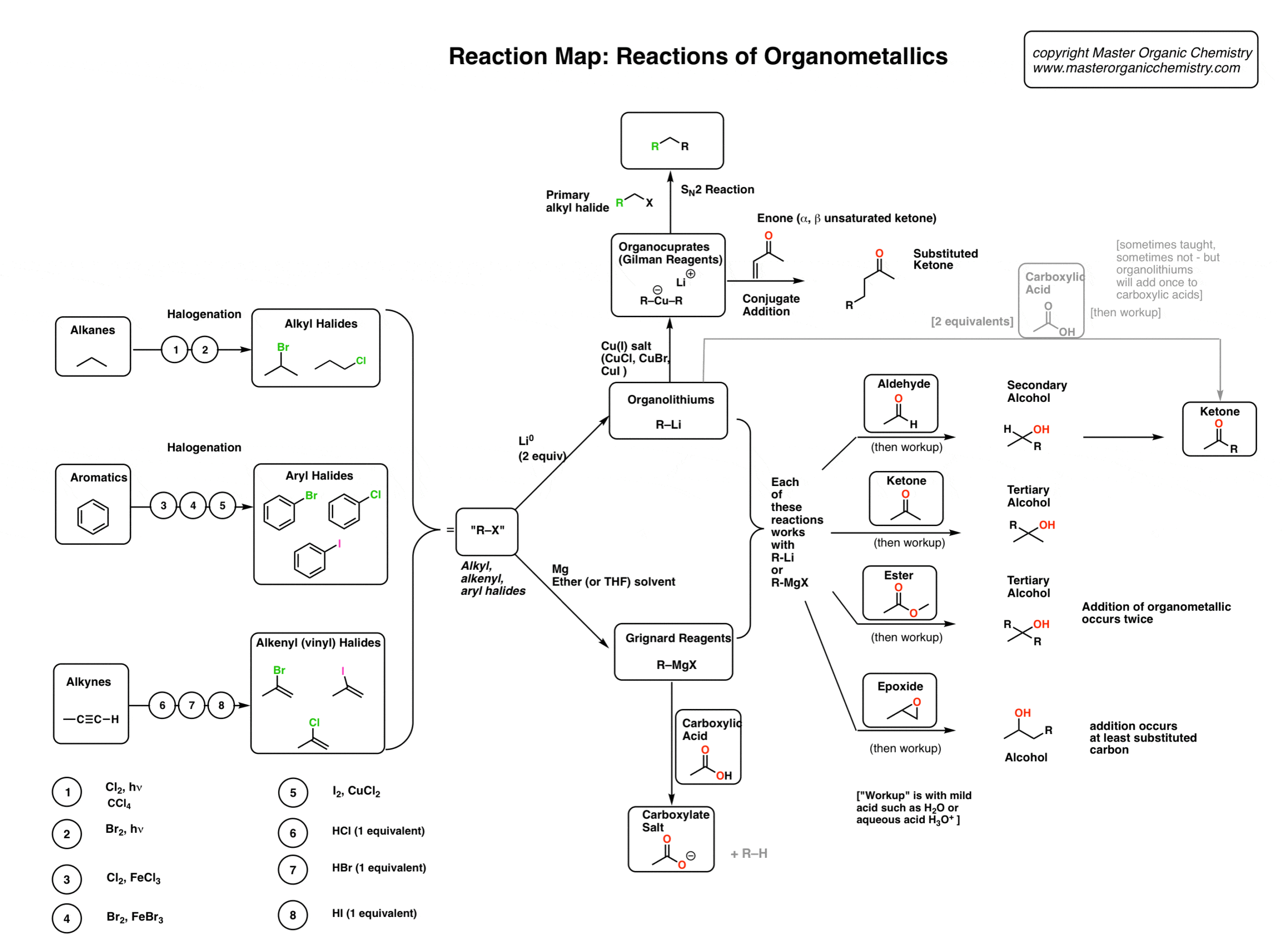
Halogenation of Alkenes
When alkenes (also known as olefins) are treated with bromine (Br2) or chlorine (Cl2) in an inert solvent [Note 1] such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) or dichloromethane (CH2Cl2), they are converted into dihalides (specifically, ‘vicinal’ dihalides since the C-halogen bonds are on adjacent carbons). This reaction results in the formation of two new
Halogenation Is Stereoselective For Anti- Addition Products
Halogenation of alkenes is an example of a stereoselectivereaction. The reaction of Br2, Cl2 and other halogens with alkenes leads to products of anti– addition. A classic example is the bromination of cyclohexene (below), which gives trans-1,2-dibromocyclohexane as a racemic mixture. No cis-1,2-dibromocyclohexane is formed. The terms syn– and anti
Halonium Ions
OK. So how does halogenation of alkenes actually work? One initial idea was that they might proceed through a free carbocation intermediate, like the addition of HCl to alkenes. [See article – Markovnikov Addition of HCl to Alkenes]. An interesting test of this theory came from halogenation of the alkene below. cis-di-t-butylethylene has a lot of s
Halogenation of Alkenes – The Mechanism
So the first step in halogenation of alkenes is formation of a halonium ion. In the second step of halogenation, the halide ion attacks the carbon from the backsideof the C-halogen bond, resulting in formation of C-halogen and breakage of C-halogen. This key step accounts for the high stereoselectivity of halogenation for the observed anti products
Halohydrin Formation – with Water and Alcohols
When bromination of alkenes is carried out in the presence of water (often as a co-solvent), halohydrinproducts are formed. A halohydrin is a molecule containing C-OH and C-halogen bonds on adjacent carbons. The reaction also proceeds through a halonium ion intermediate. As with halogenation, anti- addition products are formed exclusively. One diff
Mechanism of Halohydrin Formation
As with halogenation, the first step in halohydrin formation is creation of a halonium ion. In addition to Cl2, Br2, and I2, this can also be done with sources of electropositive halogen such as N-bromosuccinimide (NBS). [See article – N-Bromosuccinimide] After formation of the halonium ion, the next step is attack on the halonium ion by H2O, at th
Haloethers
Similarly, if alcohols are used as solvent, haloethers may form. The formation of haloethers passes through an identical mechanism to that of halohydrins. See if you can predict the product of the following reaction. An interesting wrinkle in haloether formation is the possibility for intramolecularreactions. For example, treating this alkene with
Some Applications of Halogenation Reactions
It’s worth knowing how some of these reactions can be applied later on in the course. Alkynes can be converted into cis-dihaloalkenes through treatment with halogens (See article: Halogenation of Alkynes) There is no direct way to convert an alkene to an alkyne, but they can be indirectly converted to alkynes through formation of a dihalide followe
Summary
Remember this reaction and remember this mechanism It bears a lot of similarity to other mechanisms you will encounter in the chapter on alkenes, such as: 1. Oxymercuration (Markovnikov-selective, also goes through a cyclic, 3-membered “mercurinium ion” intermediate) 2. Opening of epoxides under acidic conditions (also undergoes addition at the mo
Notes
Note 1. “Inert solvent” here just means a solvent that won’t react with the halonium ion intermediate. CCl4 and CH2Cl2 leave halonium ions alone; H2O, alcohols, and carboxylic acids can potentially undergo reactions with them. Note 2. Here are some specific examples of iodination and fluorination: Note 3. Halonium ions are not fictional chemical en

Alkene + Br2 + H2O

Halohydrin Formation

Testing Alkenes With Bromine Water Chemical Test Chemistry FuseSchool
|
Polarizability Effects and Dispersion Interactions in Alkene-Br2 ?
Polarizability Effects and Dispersion Interactions in Alkene-Br2 ?-Complexes. Cinzia Chiappe* |
|
Halogens Add Stereospecifically to Alkenes
In fact the evidence that a bromonium ion was involved in alkene Br2 |
|
Direct evidence for bromine-olefin charge-transfer complexes as
between Br2 and a series of reactive olefins including cyclohexene |
|
5.2 REACTIONS OF ALKENES WITH HALOGENS
Bromine addition can occur by a variety of mechanisms depending on the solvent |
|
Electrophilic Addition Reactions.pdf
The electrophile adds first to the alkene dictating the regioselectivity. Reagent : normally the halogen (e.g. Br2) in an inert solvent like methylene. |
|
1 Chapter 7: Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis Electrophilic
Addition of Halogens (X2) to Alkenes: 12-dihalides alkene. "X-OH". X. OH anti stereochemistry. Br2 |
|
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
The reaction of bromine with an alkene is a particularly useful qualitative test for the presence of a carbon–carbon double bond. If we dissolve bromine in |
|
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – PRACTICE EXERCISE Alkene reactions
Alkene reactions and mechanisms. FOR QUESTIONS 1-24 Br2. O. Br. + HBr. 27) Provide a detailed |
|
Chem 267: Cyclohexene (revised 6/2020) Your first formal report will
One such reaction is with bromine (Br2) in dichloromethane (CH2Cl2). The reaction of an alkene with bromine to yield a trans-12-dibrominated product. |
|
The title alkene (1) reacts with bromine in methanol; in the presence
The title alkene (1) reacts with bromine in methanol; in the presence of silver acetate to give a high yield of a crystalline 2 |
|
Electrophilic Addition Reactions - La Salle University
Halogenation of Alkenes Reaction type: Electrophilic Addition Summary • Overall transformation : C=C to X-C-C-X • Reagent : normally the halogen (e g Br2) |
|
Halogens Add Stereospecifically to Alkenes
In fact, the evidence that a bromonium ion was involved in alkene addition Br2, CH2Cl2 Br The addition of bromine to alkenes is a stereospecific reaction |
|
52 REACTIONS OF ALKENES WITH HALOGENS
Addition of Chlorine and Bromine Halogens undergo addition to alkenes The products of these reactions are vicinal dihalides Vicinal (Latin vicinus, for “ neighbor |
|
10-17-19 Reactions of Alkenes - MSU chemistry
17 oct 2019 · Most characteristic reaction of alkenes is addition to the carbon-carbon If Br2 or Cl2 is added to an alkene in the presence of water (HOH) or |
|
CHEM 109A
2 mar 2018 · No summary of reactions electrophilic addition; element element Br2 Br Br Br2 Racemic Mixture is Formed from Simple Alkenes HBr + Br |
|
1 Chapter 7: Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis Electrophilic
alkene "X-OH" X OH anti stereochemistry Br2, H2O + HBr Organic molecules are sparingly soluble in water as solvent The reaction is often done in a mix of |
|
Summary of Alkene Reactions, Ch 8 Memorize Reaction
Chem 350 Jasperse Ch 8 Handouts 2 Orientation Stereo Mechanism 8 Br CH3 H Br Br2 (or Cl2) None Trans Be able to draw completely 9 OH CH3 H |
|
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
The most characteristic reaction of alkenes is addition to the carbon–carbon Chlorine (Cl2) and bromine (Br2) react with alkenes at room temperature by the |
|
1 X2 Addition to Alkenes: Bromination of trans-Stilbene - Web Pages
Molecular bromine (Br2) is a brown, highly corrosive, fuming liquid Rather than use it directly, Br2 will be generated in situ in this reaction from the reaction of |
|
Reactions of Alkenes
of Alkenes Chapter 6 2 Step 1: Proton transfer from HBr to the alkene gives a atoms add from the opposite face of the double bond CH3 CH=CHCH3 Br2 |








![24 alkene metathesis - [PDF Document] 24 alkene metathesis - [PDF Document]](https://demo.vdocuments.mx/img/378x509/reader018/reader/2020011115/577cd6d11a28ab9e789d5462/r-2.jpg)
![Alkenes PDF - [PDF Document] Alkenes PDF - [PDF Document]](https://demo.pdfslide.net/img/742x1000/reader019/reader/2020031918/5b42e7977f8b9a26268b6ff8/r-2.jpg?t\u003d1612426163)